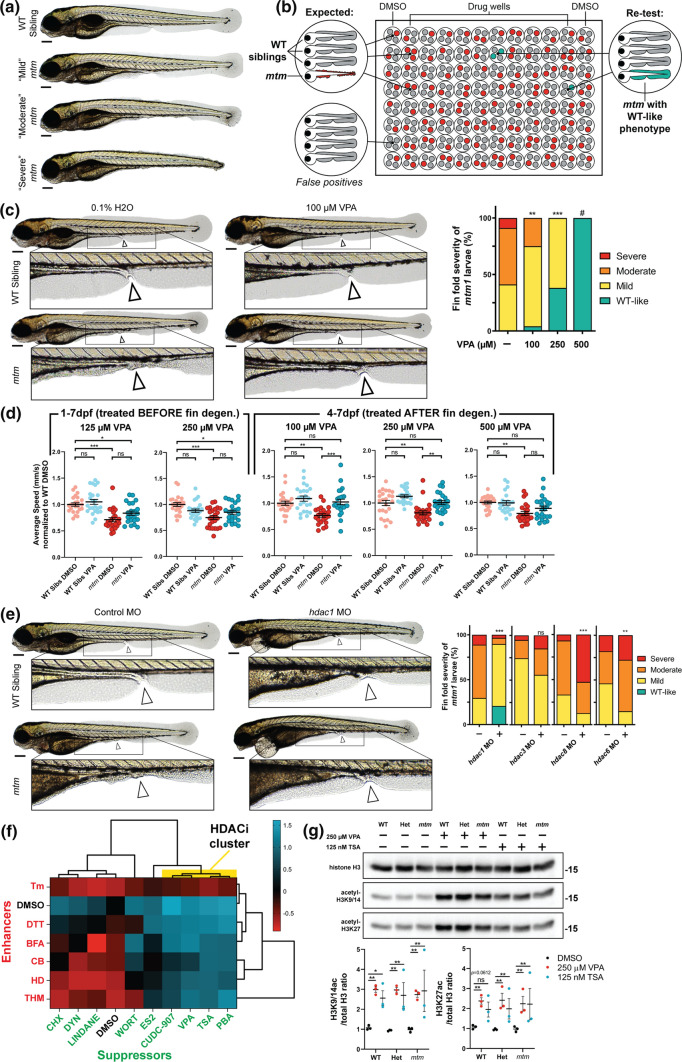
Fig. 1
Phenotypic screen of mtm mutants identifies sodium valproate (VPA) as a suppressor of fin degeneration. a mtm1?8/?8 mutants (mtm) exhibit a spectrum of larval fin fold degeneration at 4 dpf, ranging from mild to severe. b Schematic of the unbiased screen designed to identify chemicals that suppress mtm fin degeneration. In total, 1280 chemicals were screened. c VPA was identified as a suppressor in the screen when larvae were exposed from 1 to 4 dpf. Escalating VPA concentrations show increasing effectiveness in suppressing fin degeneration. (Kruskal?Wallis test with Dunn?s post-test; Mean?±?SEM; n?=?68,24,21,0). #Note: no mutants were identified at 500 ?M concentration; however there is considerable developmental toxicity at this concentration. 1 mM VPA is lethal to all fish exposed from 1 to 4 dpf. d VPA exposure promotes improvement in the motor activity of mtm mutants (2-way ANOVA with Tukey?s post-test; n?=?22?24 larvae each group). To account for a potential advantage of having intact fin folds due to rescue by VPA, motor behavior was assessed after fins degenerated using severe mtm larvae only. e Morpholino knockdown of hdac1 (zebrafish ortholog of human HDAC1/2) suppresses fin degeneration in mtm mutants. However, knockdown of class I hdac3 and hdac8, or class II hdac6, failed to suppress the phenotype (two-tailed Mann?Whitney test; n?=?29?90). f Chemical-chemical fingerprint reveals a common mode of action between VPA and HDAC inhibitors PBA, TSA (trichostatin A), and CUDC-907 in suppressing the fin phenotype (HDACi cluster in yellow) when combined with ?enhancer? chemicals that worsen mtm fin degeneration. Other suppressors do not overcome the effects of enhancers, suggesting different mechanisms of suppression are involved. g Western blot reveals that larvae exposed to VPA and TSA have elevated levels of acetylated histones, consistent with HDAC inhibitor activity. Statistics: *p?<?0.05, **p?<?0.01, ***p?<?0.001