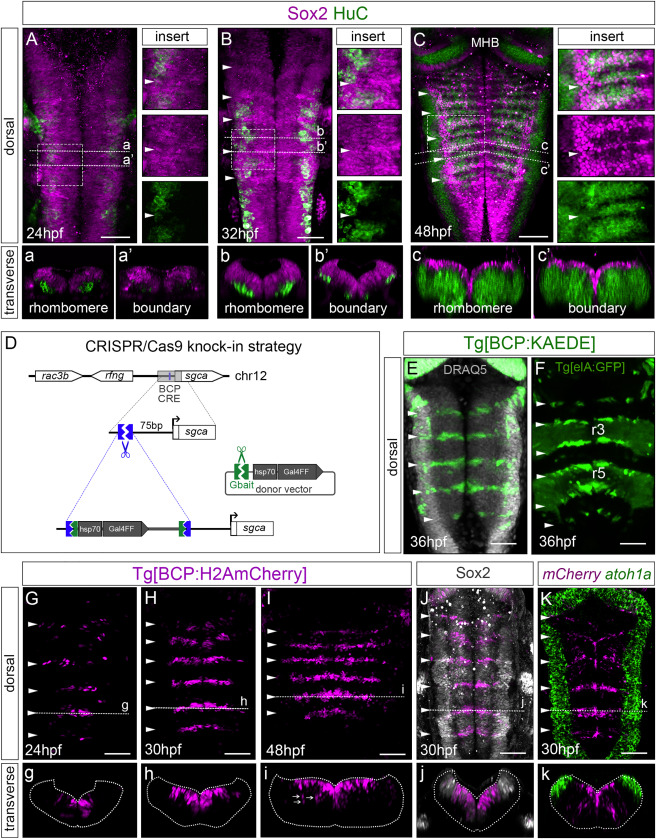
Fig. 1 Figure 1. Neurogenesis in boundary cells is delayed compared to neighboring rhombomeres (A?C) Embryos at indicated stages stained with Sox2 (magenta) and HuC (green). Inserts are magnifications of framed regions in (A)?(C), with single or overlayed channels. Note boundaries displaying higher accumulation of Sox2. (a?c, a??c?) Transverse single-stack views of rhombomeres or boundaries. (D) Scheme depicting the CRISPR-Cas9-based knockin strategy to generate the Tg[BCP:Gal4] fish line. (E and F) Tg[BCP:KAEDE] embryos expressing KAEDE in the hindbrain boundaries. Cell nuclei are in gray. Tg[elA:GFP] expresses GFP in r3 and r5. (G?I, g?i) Spatiotemporal characterization of the Tg[BCP:H2AmCherry] line. White arrows in (i) indicate neuronal derivatives of boundary cells. (J) Tg[BCP:H2AmCherry] embryo stained with Sox2 in gray (boundary cells labeled by the knocked-in reporter; magenta). (K) Double in situ hybridization of Tg[BCP:H2AmCherry] embryos with mCherry and atoh1a. (A?C; E?K) Dorsal maximum intensity projections (MIP) with anterior to the top. (g?k) Transverse views of (G)?(K) as MIP of the indicated boundary (dashed line). Position of boundaries was identified by the morphological bulges (white arrowheads; Calzolari et al., 2014). BCP, boundary cell population; MHB, mid-hindbrain boundary; hpf, hours post-fertilization; ov, otic vesicle; rl, rhombic lip. Scale bar, 50 ?m.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Cell Rep.