Image
Figure Caption
Figure 2
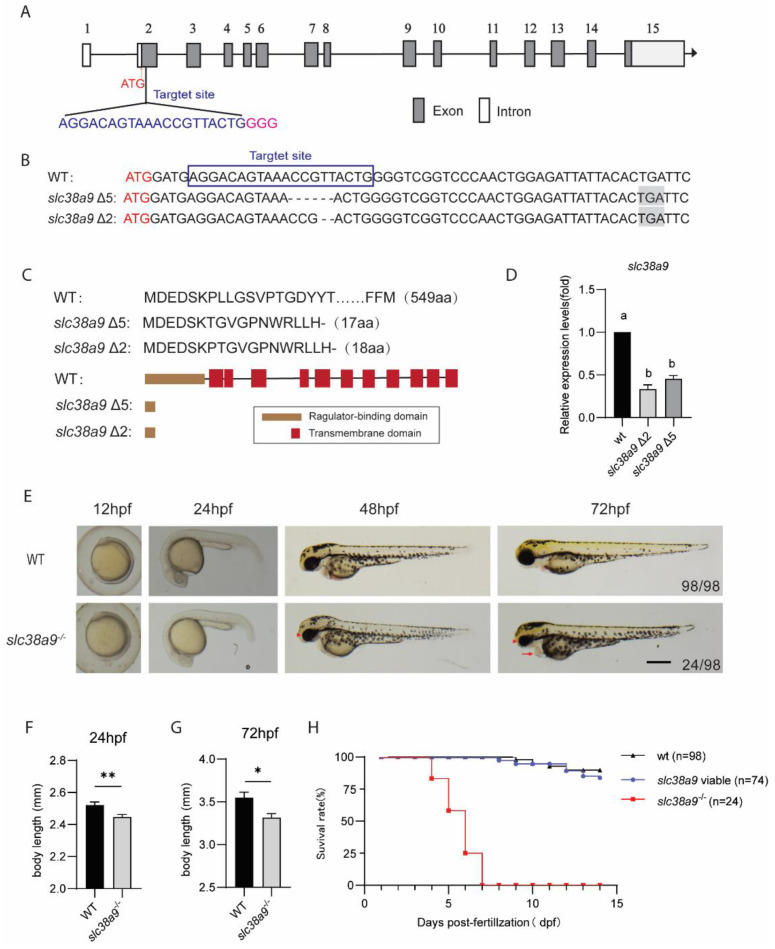
Figure 2. Knockout slc38a9 cause developmental defects in zebrafish. (A) Zebrafish slc38a9 gene structure. The selected Cas9 target sites sequence (blue) is in the second exon of the zebrafish slc38a9 gene. The PAM sequence is colored in pink. (B) The sequencing trace data of wild type and slc38a9 mutant alleles. The black shade is a premature stop codon. (C) The upper panel is the SLC38a9 protein sequences of WT and mutants. The lower panel is the schematic of the predicted SLC38A9 protein domains of WT and mutants. (D) Relative expression levels of slc38a9 mRNA in mutant and WT zebrafish at 3 dpf. The mRNA levels of slc38a9 were measured by qRT-PCR and normalized by ?-actin mRNA levels. Data shown are mean ± SEM, n = 3. Different letters indicate significant differences at p < 0.05. (E) Live images of WT and mutant at the indicated developmental stage. The Arrowhead indicates the smaller eyes of the mutant, and arrow indicates the edematous pericardial cavity of the mutant. Scale bar = 500 ?m. (F, G) The body length of mutant zebrafish was shorter than WT at 24 and 72 hpf. Data shown are mean ± SEM, n = 10. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (H) Viability of wild type and slc38a9 mutant larvae.
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Int. J. Mol. Sci.