Fig. 2
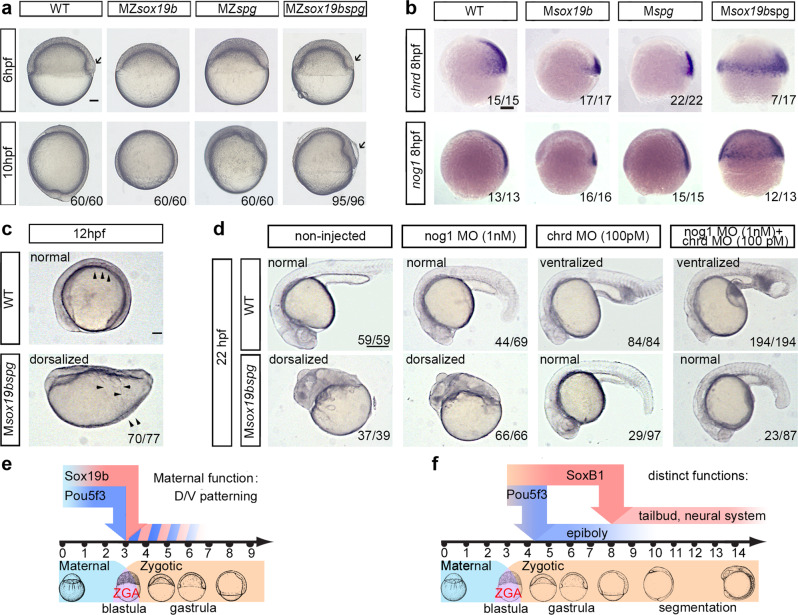
a Comparison of the single mutants, double mutant and wild-type embryos. 10 hpf: MZsox19bspg mutants are arrested in gastrulation similarly to MZspg. Arrow shows abnormally enlarged shield in MZsox19bspg. b, c Double maternal mutants Msox19bspg are dorsalized. b In situ hybridization for dorsal markers noggin1 and Chordin, lateral views, dorsal to the right. Note the circumferential expansion in the Msox19bspg. c Somites (arrowheads) form on the dorsal side in WT, but spread over the Msox19bspg embryo. Dorsal up, anterior to the left. d Normal development of Msox19bspg mutants can be rescued by reducing Chordin, but not Noggin1 levels. The wild-type or Msox19bspg embryos were injected with the indicated morpholinos or non-injected. The numbers show the ratio of embryos with indicated phenotype/ all embryos alive at 22 hpf. The arrows show abnormally expanded blood progenitor cells in the ventralized wild-type embryos. Anterior to the left, dorsal up. e, f Combinatorial (e) and distinct (f) functions of Pou5f3 and SoxB1. e Maternal Sox19b and Pou5f3 safeguard correct D/V patterning. f Pou5f3 is critical for epiboly and gastrulation, redundant action of zygotic SoxB1 (Sox19a, Sox19b, Sox2, and Sox3) is critical for organogenesis. Scale bars in a, b, c: 100 Ám, in d: 200 Ám.