Figure 5
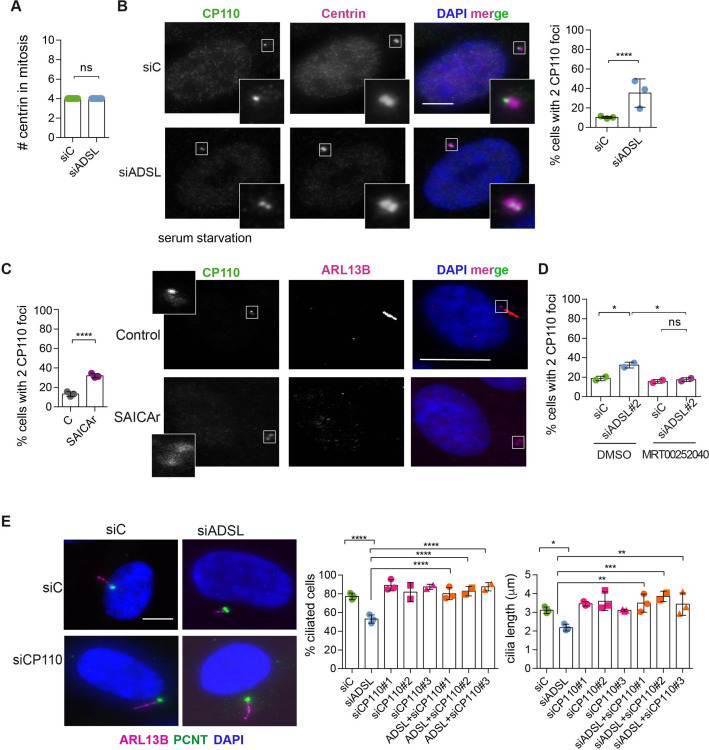
(A) Quantification of the number of centrin foci present in mitotic RPE-1 cells transfected with control or ADSL smart pool siRNAs for 96 hr (n = 2, two-tailed t-test, ns not significant). (B) ADSL-silenced cells and controls were stained for centrin (magenta) and CP110 (green). Nuclei are shown by DAPI (blue). Graph depicts the number of ciliated cells with two CP110 foci per centrosome (n = 3, scored 342 cells for siC, 221 cells for siADSL, *p<0.05). (C) Cells mock or treated with SAICAr were processed and analyzed as described in panel (B) (n = 3, scored 288 cells for control and 253 cells for SAICAr, ***p<0.001). (D) RPE-1 cells depleted with ADSL or control siRNAs were treated with vehicle or MRT00252040 and stained as in (B, C). Graph depicts the percentage of cells presenting two CP110 foci per centrosome (n = 2; scored 177 cells for siC + DMSO, 180 cells for siADSL + DMSO, 75 cells for siC + MRT00252040, 78 cells for siADSL + MRT00252040, *p<0.05). (E) RPE-1 cells depleted with ADSL and/or CP110 (silenced for 24 hr with three different siRNAs) were serum starved for 48 hr, fixed, and stained for ARL13B (magenta) and pericentrin (PCNT) (green). Graphs show the number of ciliated cells (n = 3 for siC, siADSL, siCP110#1, siADSL + siCP110#1; n = 2 for siCP110#2, siCP110#3, siADSL + siCP110#2 and siADSL + siCP110#3, scored 461 cells for siC, 301 cells for siADSL, 277 cells for siCP110#1, 289 cells for siADSL + siCP110#1, 119 cells for siCP110#2, 90 cells for siADSL + siCP110#2, 141 cells for siCP110#3, 98 cells for siADSL + siCP110#3, ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001) and cilia length (n = 3, one-way ANOVA ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05). All graphs show means ± SD with individual values shown in circles.
Adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL) depletion and SAICAr impair CP110 removal.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Elife