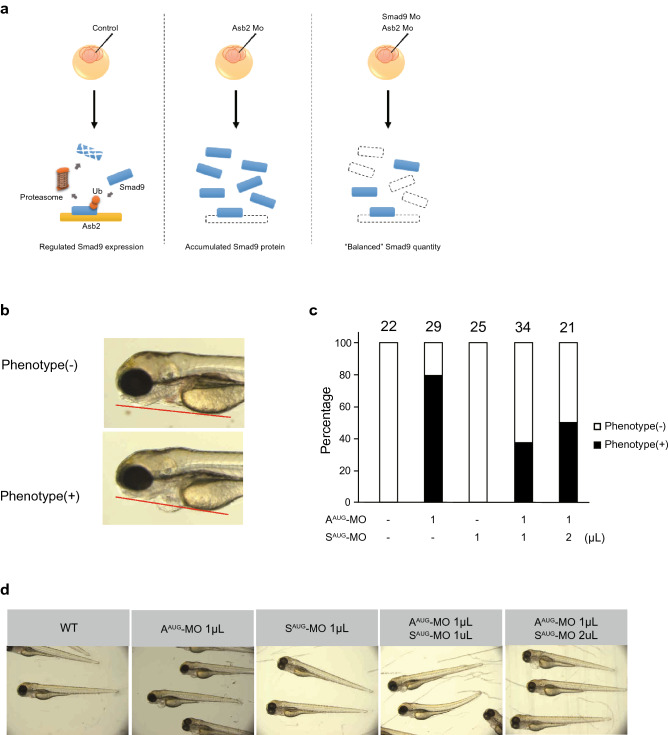
Figure 5
The phenotype of Asb2 knockdown is rescued by simultaneous knockdown of Smad9. (a) Scheme of the experimental hypothesis. The balanced amount of Smad9 protein is enabled by expression as well as degradation of Smad9. The injection of Asb2 Mo may result in loss of active degradation of Smad9 protein leading to the accumulation of Smad9. Simultaneous knockdown of Asb2 and Smad9 may attenuate the accumulation of Smad9 protein. Therefore, MO targeting the start codon of Asb2 (AAUG-MO) and/or Smad9 (SAUG-MO) was injected into zebrafish embryos at the 2–4 cell stage. At 72 hpf, the phenotype of the embryos was determined. (b) The cardiac phenotype was determined to be positive when the pericardium showed remarkable swelling over the tangent line of yolk and mandible. (c) The ratio of embryos with positive (black) and negative (white) phenotypes. The number of the animals is shown above each bar. (d) Representative animals of each group. No obvious phenotype was detected in any group.