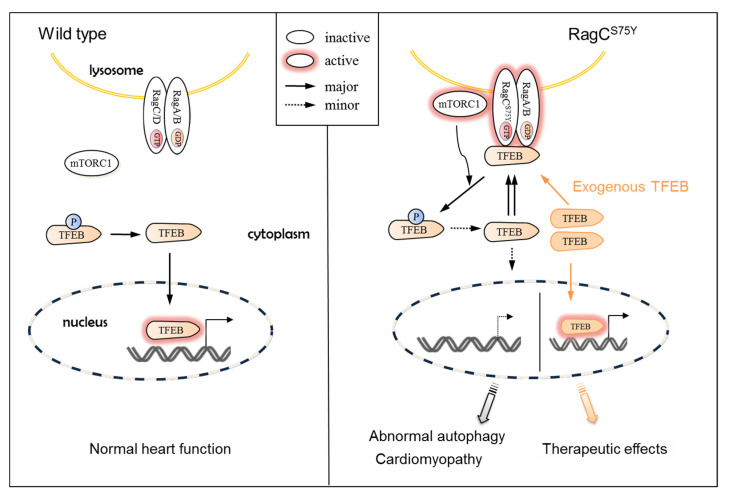
Figure 8 Schematic mechanism of RagCS75Y cardiomyopathy and a candidate therapeutic strategy. (Left) Under full nutrients condition, the wild type heterodimeric Rags (formed by either RagA or RagB and RagC and RagD) is in the inactive state, leading to mTORC1 detachment from the lysosome and to its inactivation. TFEB is dephosphorylated and able to translocate to the nucleus, where it activates gene expression programs that boost lysosomal function and autophagy. (Right) The S75Y mutation drives Rags to be active, which recruits mTORC1 and TFEB to the lysosome surface, where phosphorylation of TFEB by active mTORC1 happens. The TFEB cycles between cytoplasm and the lysosomal surface limits its nucleus translocation, which triggers cascades of pathological changes, such as dysregulated autophagy, which ultimately result in cardiomyopathy. Exogenous expression of TFEB is an effective therapeutic strategy that restores nucleus translocation of TFEB and ameliorates RagCS75Y cardiomyopathy.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Int. J. Mol. Sci.