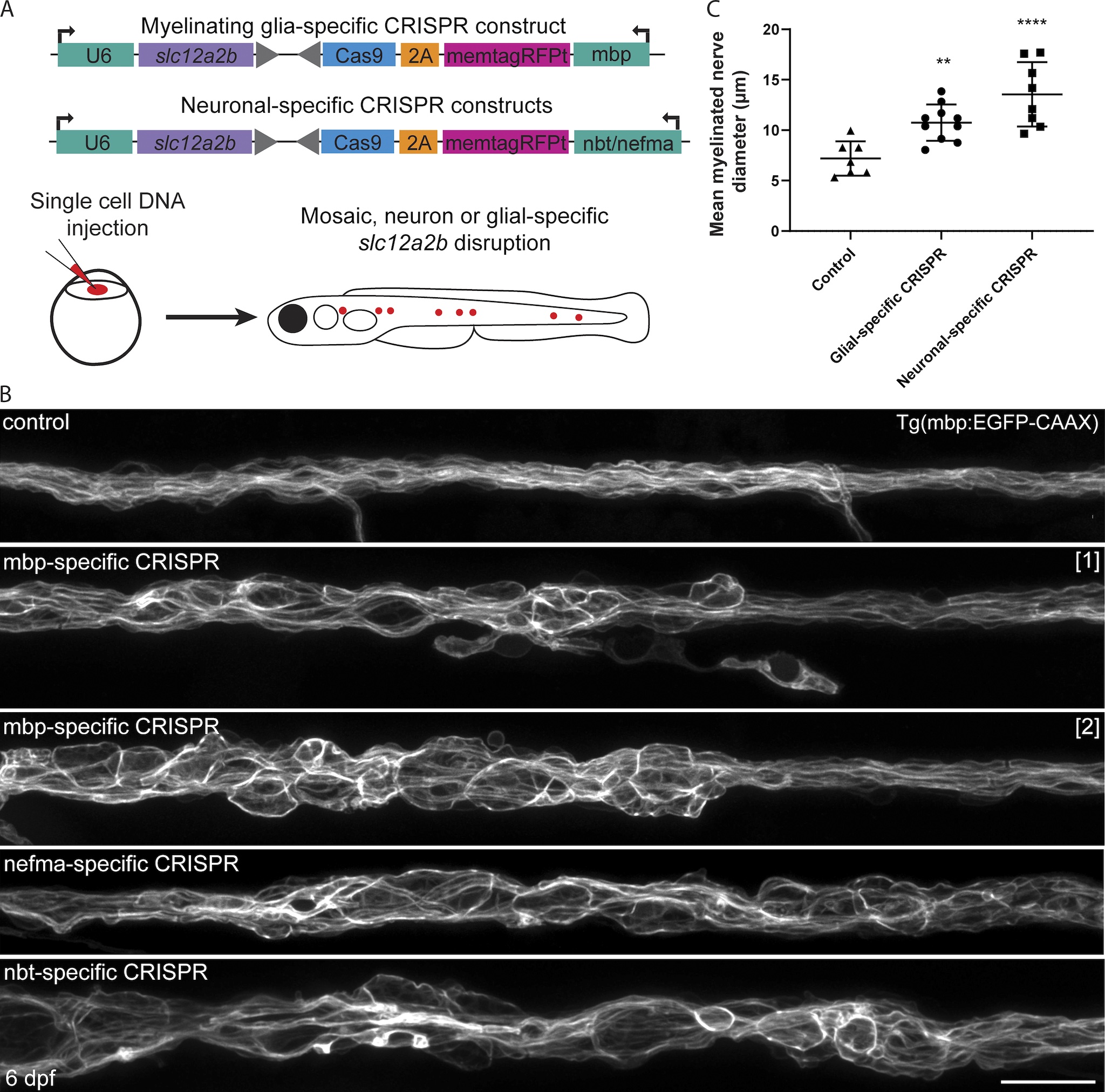
Fig. 3 Cell-type?specific disruption of slc12a2b in either neurons or Schwann cells leads to myelin pathology. (A) Schematic overviews of constructs used to induce slc12a2b mutations in myelinating glial cells (top) and neurons (bottom), which are separately injected into embryos at the single-cell stage, leading to mosaic expression (red dots) at later stages, when myelination is examined. (B) Confocal images of Schwann cells along the pLLn in a 6 dpf Tg(mbp:EGFP-CAAX) control (top), two genetically mosaic animals in which slc12a2b has been targeted in myelinating glial cells, and two further mosaic animals in which slc12a2b has been targeted in neurons. Scale bar, 20 Ám. (C) Quantitation of mean myelinated nerve diameter in controls compared with larvae with glial- or neuronal-specific slc12a2b-specific disruption at 6 dpf (control 7.2 ▒ 1.7 Ám vs. glial-specific slc12a2b disruption 10.7 ▒ 1.8 Ám vs. neuronal-specific slc12a2b disruption 13.6 ▒ 3.2 Ám). Error bars represent mean ▒ SD. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey?s multiple comparison test was used to assess statistical significance (ANOVA F(2,22) = 14.09, P = 0.0001). Each point represents an individual animal. **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ J. Cell Biol.