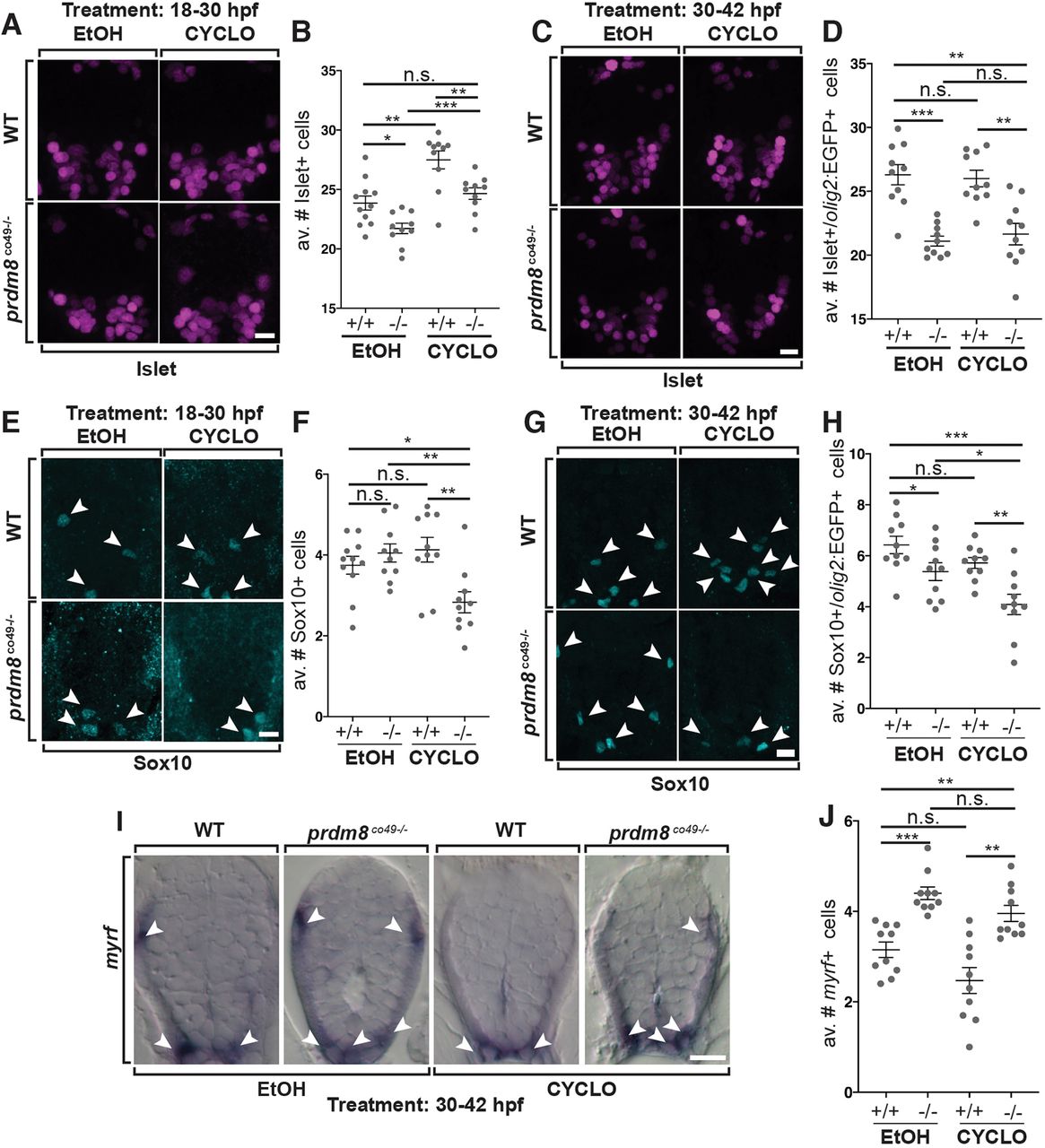
Fig. 10 Shh inhibition rescues the motor neuron but not oligodendrocyte phenotypes of prdm8 mutant embryos. (A,C,E,G) Representative images of trunk spinal cord sections from 48 hpf embryos treated with 0.5 μM cyclopamine (CYCLO) or ethanol (EtOH) from 18 to 30 hpf (A,E) or 30 to 42 hpf (C,G), and processed to detect Isl (A,C) or Sox10 (E,G) expression. (A,B) Wild-type (WT) embryos treated with EtOH control solution and prdm8 mutant embryos treated with cyclopamine have similar numbers of motor neurons. (C,D) There are fewer motor neurons (Islet+) in prdm8co49−/− embryos treated with EtOH and cyclopamine compared with wild-type embryos treated with EtOH. (E,F) There are fewer OPCs (Sox10+; arrowheads) in prdm8co49−/− embryos treated with cyclopamine and no difference in OPCs prdm8co49−/− embryos treated with EtOH compared with wild-type embryos treated with EtOH. (G,H) There are fewer OPCs (Sox10+; arrowheads) in prdm8co49−/− embryos treated with cyclopamine and slightly fewer OPCs in prdm8co49−/− embryos treated with EtOH compared with wild-type embryos treated with EtOH. (I) Representative trunk spinal cord transverse sections obtained from 72 hpf larvae treated with 0.5 μM cyclopamine or EtOH from 30 to 42 hpf showing myrf mRNA expression detected by in situ RNA hybridization. (I,J) prdm8co49−/− embryos treated with EtOH or cyclopamine have more oligodendrocytes (myrf+; arrowheads) than wild-type embryos treated with EtOH. n=10 for all genotypes and treatments except for wild-type embryos treated with EtOH (n=11) (A,E). Data are mean±s.e.m. with individual data points indicated. Statistical significance was evaluated by an unpaired, two-tailed Student's t-test. *P<0.05; **P<0.001; ***P<0.0001; n.s., not significant. Scale bars: 10 μm.
Image
Figure Caption
Figure Data
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development