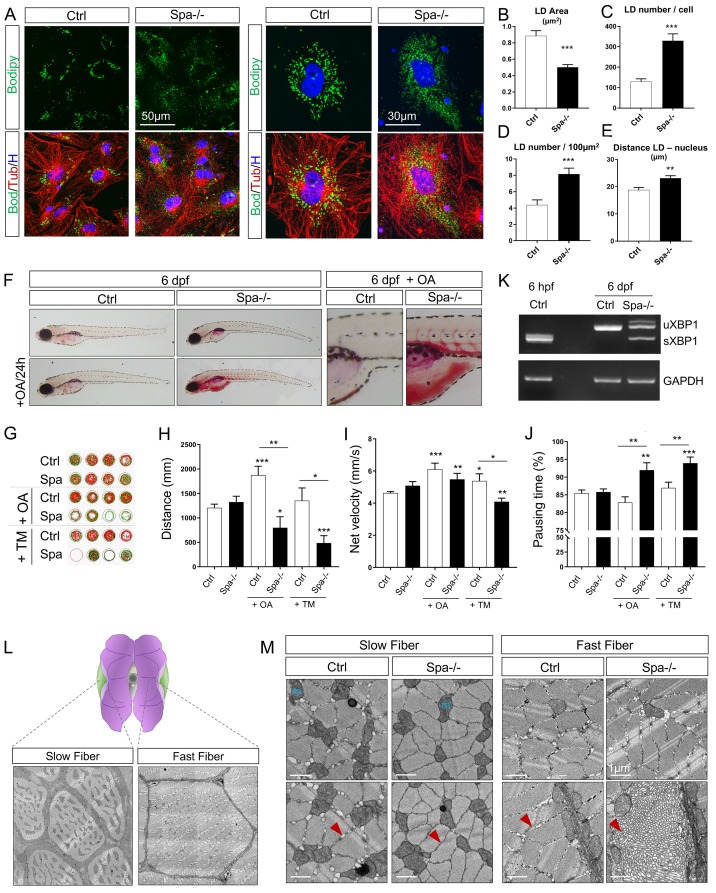
Fig 3
(A) Confocal microscopy images of zebrafish embryonic cells from wild-type and Spastin KO animals (Ctrl and Spa-/-) treated with 300μM oleic acid (OA) for 18h before acquisition. Tubulin labeling corresponds to microtubules (red), Bodipy to lipid droplets (green) and Hoechst to nucleus (blue). (B) Quantification of LD area in embryonic cells. n = 23 cells Ctrl and n = 31 cells Spa-/-. (C-D) Quantification of LD number per cell (C) or in 100μm2 (D). n = 23 cells Ctrl and n = 31 cells Spa-/-. (E) Quantification of mean distance between individual LD and nucleus center. n = 23 cells Ctrl and n = 31 cells Spa-/-. (F) Oil red O staining in 6 dpf zebrafish larvae. Wild-type and Spastin KO were compared in basal conditions or after a 24h of OA in fish water. N = 3 experiments; n = 10 embryos per group. (G-J) Locomotion analyses in 6 dpf larvae (n = 24 larvae in each group) and after 24h administration of OA or Tunicamycin (TM) in fish water (n = 12 in each group). Zebrabox quantifications based on motion detection thresholds distinguishing slow (v) and fast velocity (V) as follow: 0<v<3mm/s (green) and V<6m/s (red). (K) RT-PCR detection of XBP1 splicing in 6 dpf zebrafish. (L) Schematic representation of slow versus fast twitch skeletal muscle distribution in adult zebrafish with respective electron micrographs delineating one fiber. (M) Electron micrographs taken in 8 months zebrafish skeletal muscle. Red arrow: sarcoplasmic reticulum, m: mitochondria. Bars are mean ± SEM, *