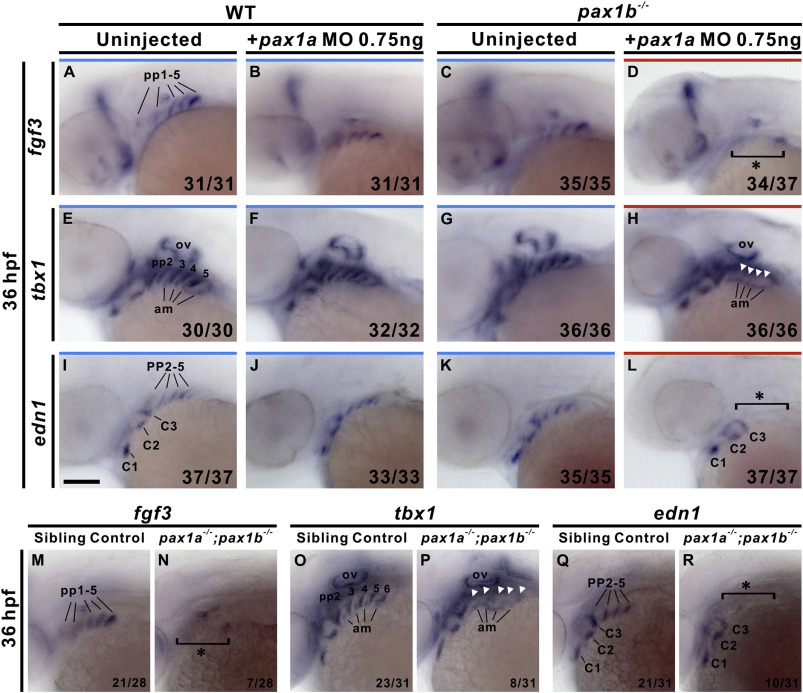
Fig. 10 pax1a- and pax1b-deficient embryos exhibit absent fgf3, tbx1 and edn1 expression in pharyngeal pouches. Absent expression of fgf3 in pharyngeal pouches (pp) 1–5 was identified in 0.75 ng pax1a MO-injected pax1b−/− mutant embryos (D) compared to uninjected wild types (WT; A), 0.75 ng pax1a MO-injected wild types (B) or uninjected pax1b−/− mutant embryos (C) at 36 hpf. Similar absent expression of tbx1 or edn1 in posterior pharyngeal pouches 2–5 were observed in 0.75 ng pax1a MO-injected pax1b−/− mutant embryos (H, L) compared to uninjected wild types (E, I), 0.75 ng pax1a MO-injected wild types (F, J) or uninjected pax1b−/− mutant embryos (G, K) at 36 hpf. Similar defects in endodermal expression of fgf3 (N), tbx1 (P) and edn1 (R) in pharyngeal pouches were also found in pax1a−/−; pax1b−/− double mutants in contrast with sibling controls (i.e., pax1a+/−; pax1b−/− or pax1a+/+; pax1b−/−) (M, O, Q) at 36 hpf. Asterisks or arrowheads indicate absent expression. Affected embryos per total number of analyzed embryos are shown. Am, adjacent mesoderm; C, mesodermal core; ov, otic vesicle. Scale bars represent 100 μm.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 161, Liu, Y.H., Lin, T.C., Hwang, S.L., Zebrafish Pax1a and Pax1b are required for pharyngeal pouch morphogenesis and ceratobranchial cartilage development, 103598, Copyright (2020) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.