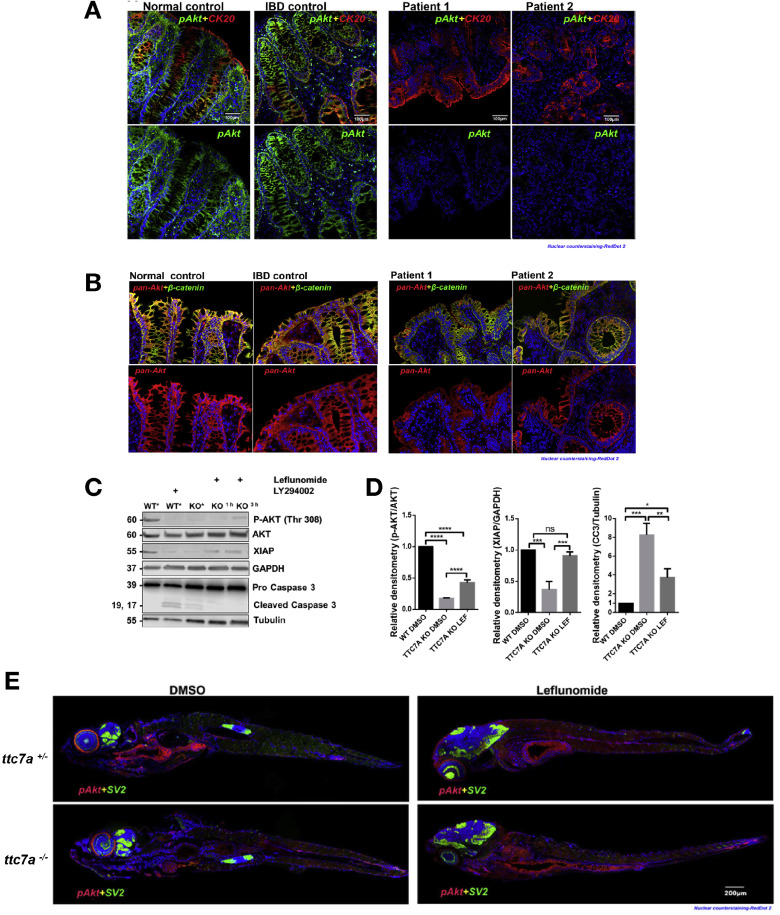
Fig. 5
p-AKT is reduced in TTC7A deficiency. (A) Histopathology analysis of p-AKT in human colon tissue. Costaining of CK20, a marker for the intestinal epithelium, and p-AKT is present in the normal and IBD control samples, whereas p-AKT is diminished in patients with TTC7A-deficiency. Patient 1 is the colonoid donor, and patient 2 is unpublished with confirmed biallelic mutations. RedDot 2 nuclear counterstain (blue). Sections were originally magnified at ×20 objective. (B) Histopathology analysis of pan-AKT (total AKT) in human colon tissue. Biopsy samples are the same as those described in Figure 5A. Pan-AKT is present in all samples, albeit with reduced intensity in the TTC7A-deficiency patient samples. Sections were originally magnified at ×20 objective. (C) Immunoblot for p-AKT, XIAP, and cleaved caspase 3 in WT and TTC7A-KO cells. After 3 hours, leflunomide treatment in TTC7A-KO cells, p-AKT, and XIAP protein levels are detectable, whereas cleaved caspase 3 is diminished. Asterisk indicates DMSO (n = 3). (D) Densitometric analysis of p-AKT, XIAP, and cleaved caspase 3 from WT and TTC7A-KO cells. One-way ANOVA with post hoc test (Tukey); *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001, ****P < .0001 (n = 3). (E) The ttc7a+/– and ttc7a–/– whole-mount zebrafish staining with p-AKT (red), synaptic vesicle protein 2 (SV2) (green), and RedDot 2 nuclear counterstain (blue). SV2 staining, indicating neuromuscular junctions, is absent from the intestinal epithelial monolayer and aids in differentiating epithelial cells from other nearby cell types. In the DMSO-treated panel, p-AKT staining (Ser473) in ttc7a+/– fish is evident along the gastrointestinal tract but absent in ttc7a–/– fish. Leflunomide treatment (3-7 dpf) restores p-AKT staining in the intestinal epithelium of ttc7a–/– fish. Fish were originally magnified at ×5 objective (n = 4).