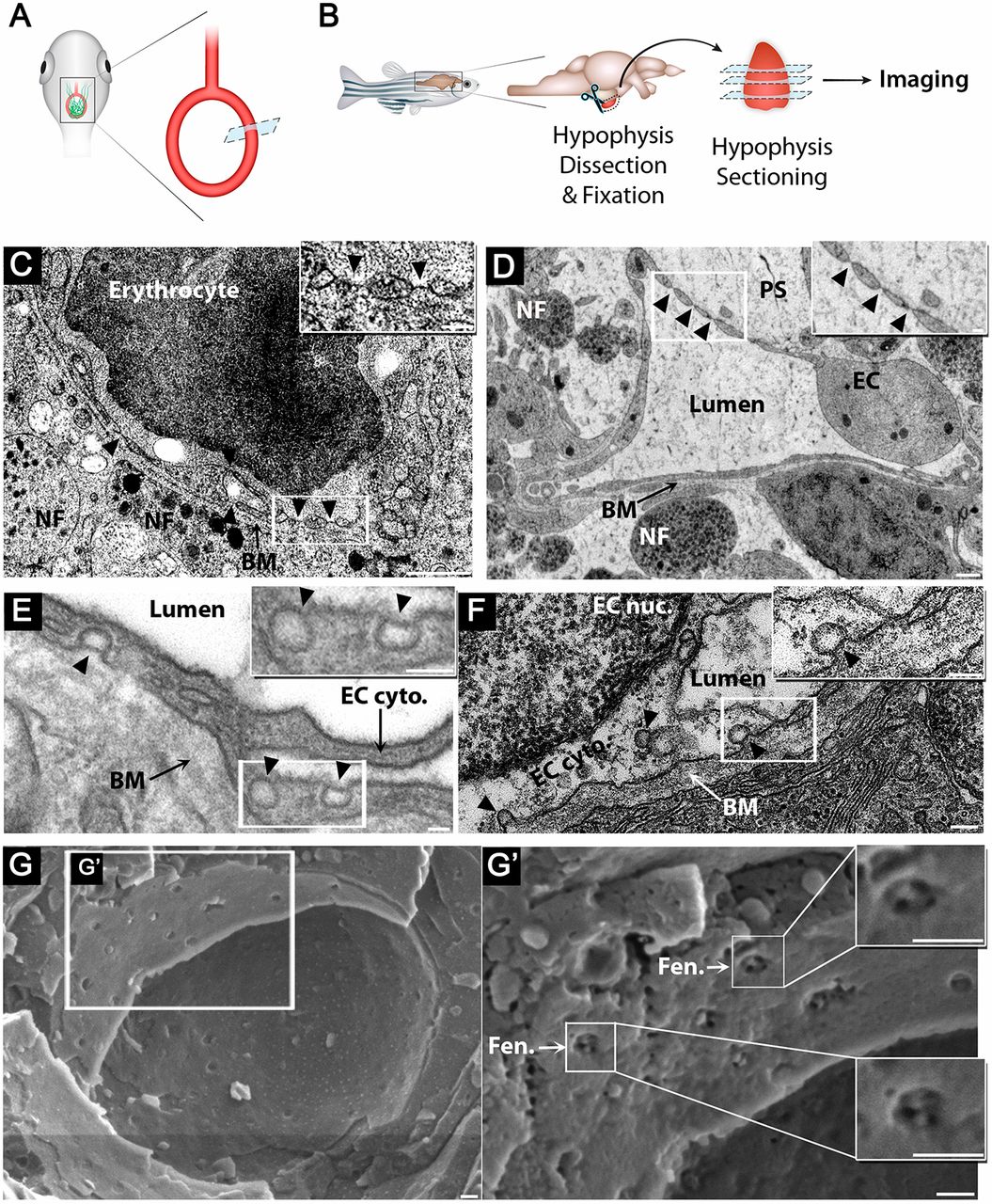
Fig. 3 Zebrafish hypophyseal endothelia contain diaphragmed fenestrae and caveolae. (A) Scheme describing TEM imaging of the hypophyseal capillary in zebrafish larvae. The hypophyseal oxtl:EGFP reporter was used as an anatomical landmark to localize the position of larval hypophysis prior to tissue preparation for TEM imaging. (B) Scheme describing TEM imaging of adult zebrafish hypophysis. Multiple ultrathin sections (60-80?nm) of the dissected hypophysis from adult zebrafish were submitted to TEM imaging. (C,D) TEM imaging of cross-section of larval (5 dpf) (C) and adult (D) showing hypophyseal fenestrated capillary contacting hypothalamic axonal nerve fibers (NF). Scale bars: 500?nm in C; 200?nm in D. Insets show higher magnification of diaphragmed fenestrae organized in a sieve-like manner. Fenestrae are indicated by arrowheads. Scale bars: 100?nm. (E,F) TEM imaging of hypophyseal endothelia containing abluminal, luminal and internalized caveolae indicated by arrowheads. Scale bars: 100?nm. Insets show higher magnification of internalized and surface caveolae with stomatal diaphragm. Scale bars: 100?nm. (G) Cryo-SEM imaging of fenestrated endothelia in adult zebrafish hypophysis. Higher magnifications (G?) of the hypophyseal fenestrated endothelial cell show the surface view of the fenestral diaphragm dissected into several openings by fibrils that converge at the center of the pore (insets). BM, basement membrane; EC, endothelial cell; EC cyto., endothelial cell cytoplasm; EC nuc., endothelial cell nucleus; Fen., fenestrae; NF, nerve fiber; PS, perivascular space. See related Fig. S1.
Image
Figure Caption
Acknowledgments
This image is the copyrighted work of the attributed author or publisher, and
ZFIN has permission only to display this image to its users.
Additional permissions should be obtained from the applicable author or publisher of the image.
Full text @ Development