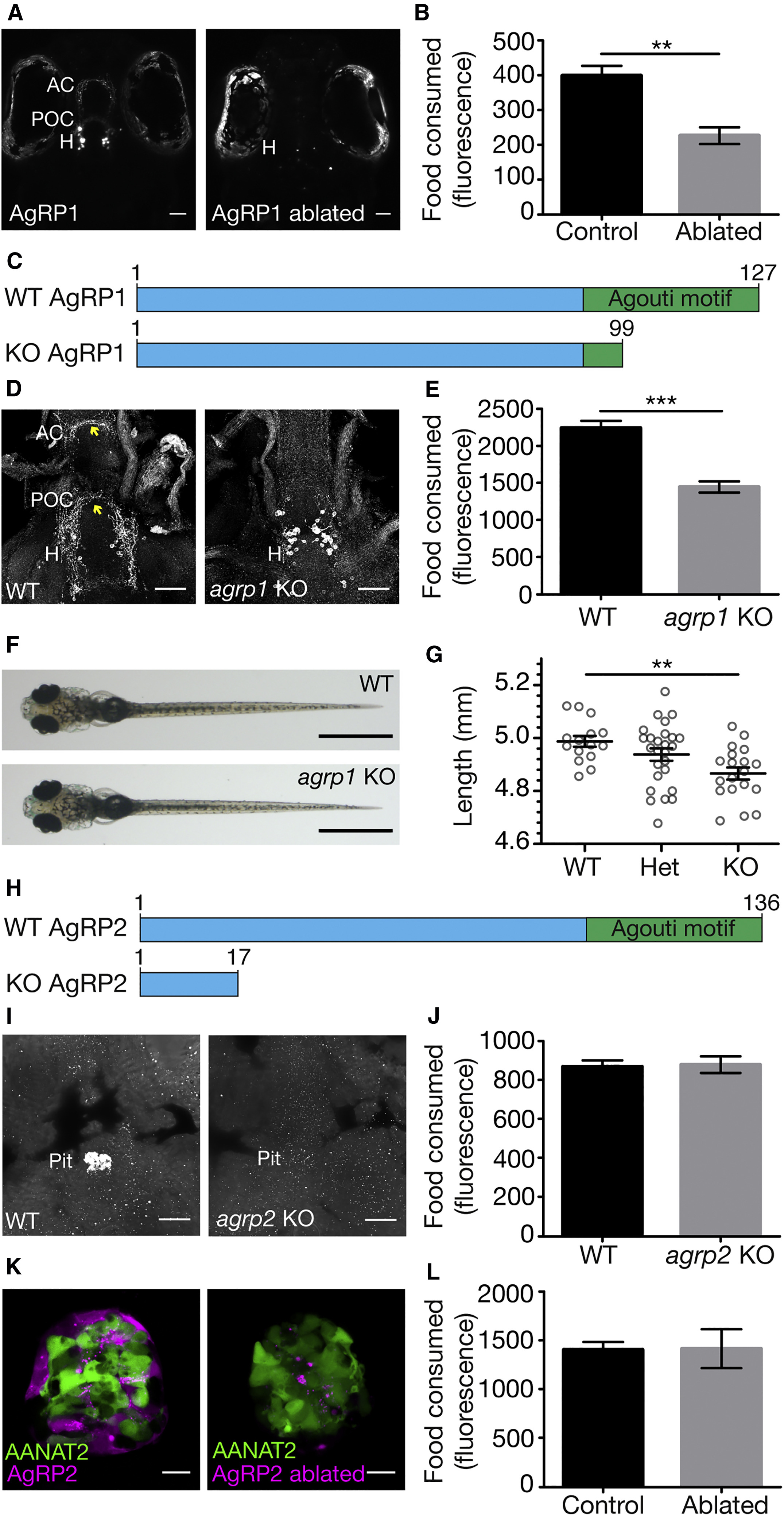
Fig. 1
AgRP1, but Not AgRP2, Is a Regulator of Feeding Behavior
(A) (Left) Dorsal view of 5-dpf larva expressing NTR-mCherry fusion protein in agrp1-expressing neurons. The cell bodies are located in the hypothalamus and project toward the post-optic commissure and the anterior commissure. (Right) The same larva at 8 dpf, after treatment with metronidazole. AgRP1 neurons were ablated, and the mCherry signal cannot be identified. AC, anterior commissure; H, hypothalamus; POC, post-optic commissure. Scale bars represent 50 μm.
(B) Quantification of the food consumed by 8-dpf AgRP1 neuron-ablated larvae and NTR-negative sibling controls (t test; n = 6; p < 0.01). Values represent the mean fluorescence intensity ± SE. See also Figure S1.
(C) Schematic illustration of the AgRP1 precursor in WT and agrp1 KO fish. The predicted WT AgRP1 contains 127 amino acids, including the C-terminal Agouti motif. The predicted mutated AgRP1 contains 99 amino acids and lacks the Agouti motif.
(D) Immunostaining analysis of AgRP1 in WT (left) and agrp1 KO (right) larvae using zebrafish-specific AgRP1 polyclonal antibody. In the mutant, as apposed to WT, the truncated AgRP1 is not transported along the axons to reach the AC and POC (arrowheads). Ventral view is shown. Scale bars represent 50 μm.
(E) Quantification of the food consumed by 8-dpf agrp1 KO and controls (progeny of WT siblings; t test; n = 9; p < 0.001). Values represent the mean fluorescence intensity ± SE.
(F) Dorsal view of 8-dpf agrp1 KO and WT sibling. Scale bars represent 1 mm.
(G) Body length measurements of 8-dpf agrp1 KO, their heterozygotes, and WT siblings (one-way ANOVA; n = 15–26; p < 0.01). Circles represent single measurements; horizontal lines represent the mean body length ± SE.
(H) Schematic illustration of the AgRP2 precursor in WT and agrp2 KO fish. The predicted WT AgRP2 contains 136 amino acids, including the C-terminal Agouti motif. The predicted mutated AgRP2 contains only 17 amino acids and lacks the Agouti motif.
(I) Immunostaining analysis of AgRP2 in WT (left) and agrp2 KO (right) larvae using the zebrafish-specific AgRP2 polyclonal antibody. Ventral view of the pituitary is shown. No signal is detected in pituitaries of mutated larvae. Pit, pituitary. Scale bars represent 10 μm.
(J) Quantification of the food consumed by 8-dpf agrp2 KO and controls (progeny of WT siblings; t test; n = 6; p > 0.05). Values represent the mean fluorescence intensity ± SE.
(K) (Left) Pineal gland of 3-dpf larva expressing NTR-mCherry fusion protein in agrp2-expressing cells and EGFP under the promoter of aanat2 (which marks the pineal photoreceptors) [20]. (Right) Same larva at 8 dpf is shown, after treatment with metronidazole. AgRP2 cells were ablated, and the photoreceptors were not damaged. Scale bars represent 10 μm.
(L) Quantification of the food consumed by 8-dpf AgRP2 neuron-ablated larvae and NTR-negative sibling controls (t test; n = 6; p > 0.05). Values represent the mean fluorescence intensity ± SE.