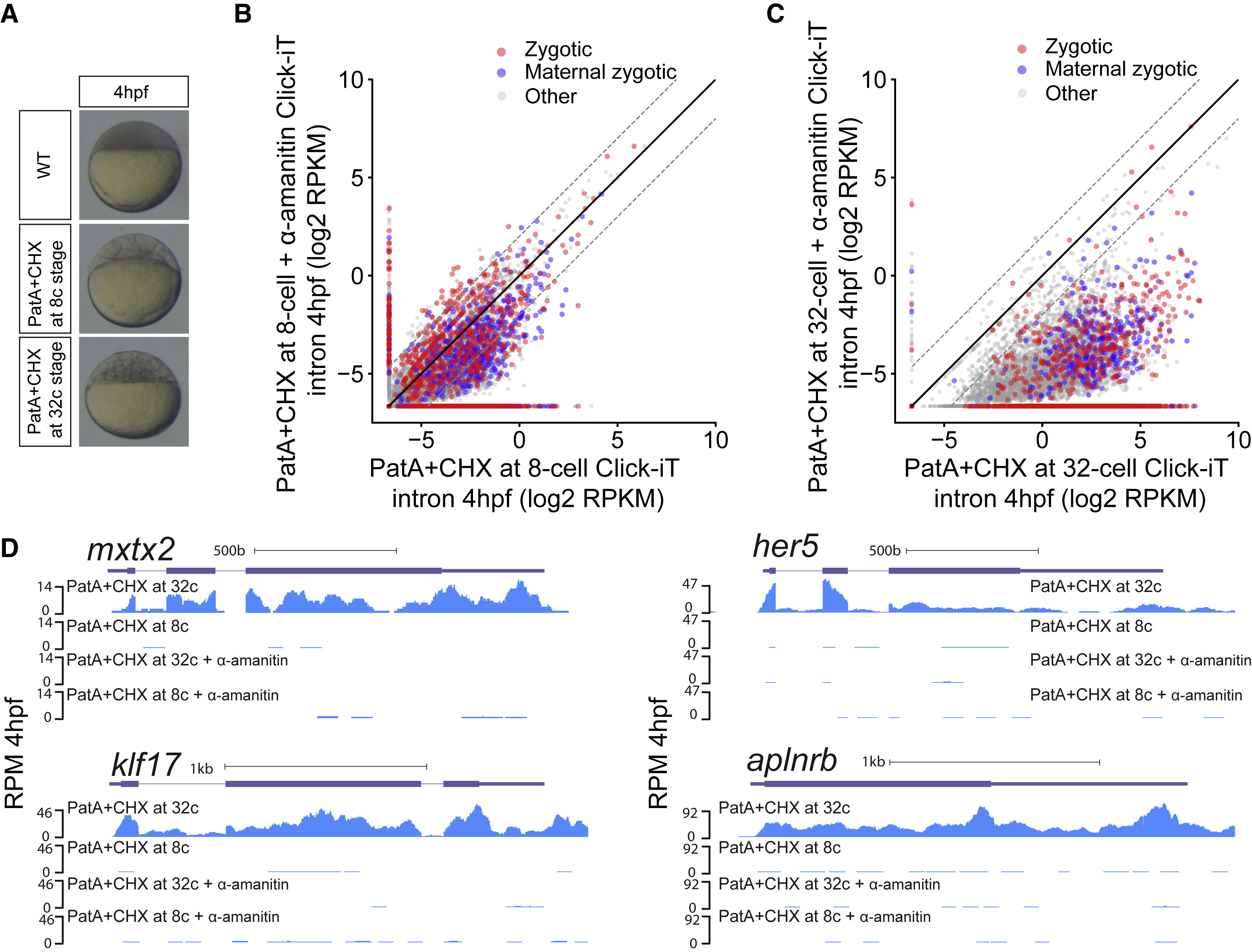
Fig. 4
Transcriptional Competency of the Zygotic Genome Depends on the Translation of Maternal mRNAs
(A) Embryos treated with pateamine A (PatA) and cycloheximide (CHX) at 8- (1.25 hpf) and 32-cell stage (1.75 hpf) arrest zebrafish embryos at 16- and 64-cell stage, respectively.
(B and C) Biplot of Click-iT-seq RNA levels at 4 hpf comparing the level of transcription using intron signal. Embryos were treated with PatA+CHX at 8-cell stage (B) or at 32-cell stage (C), with and without α-amanitin. Dashed lines represent 4-fold change.
(D) Genome tracks representing normalized Click-iT-seq signal in the embryos described in (B) and (C). Click-iT-seq was normalized by the total number of mitochondrial RNAs as an internal control. RPM (STAR Methods).
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 49, Chan, S.H., Tang, Y., Miao, L., Darwich-Codore, H., Vejnar, C.E., Beaudoin, J.D., Musaev, D., Fernandez, J.P., Benitez, M.D.J., Bazzini, A.A., Moreno-Mateos, M.A., Giraldez, A.J., Brd4 and P300 Confer Transcriptional Competency during Zygotic Genome Activation, 867-881.e8, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell