Fig. 1
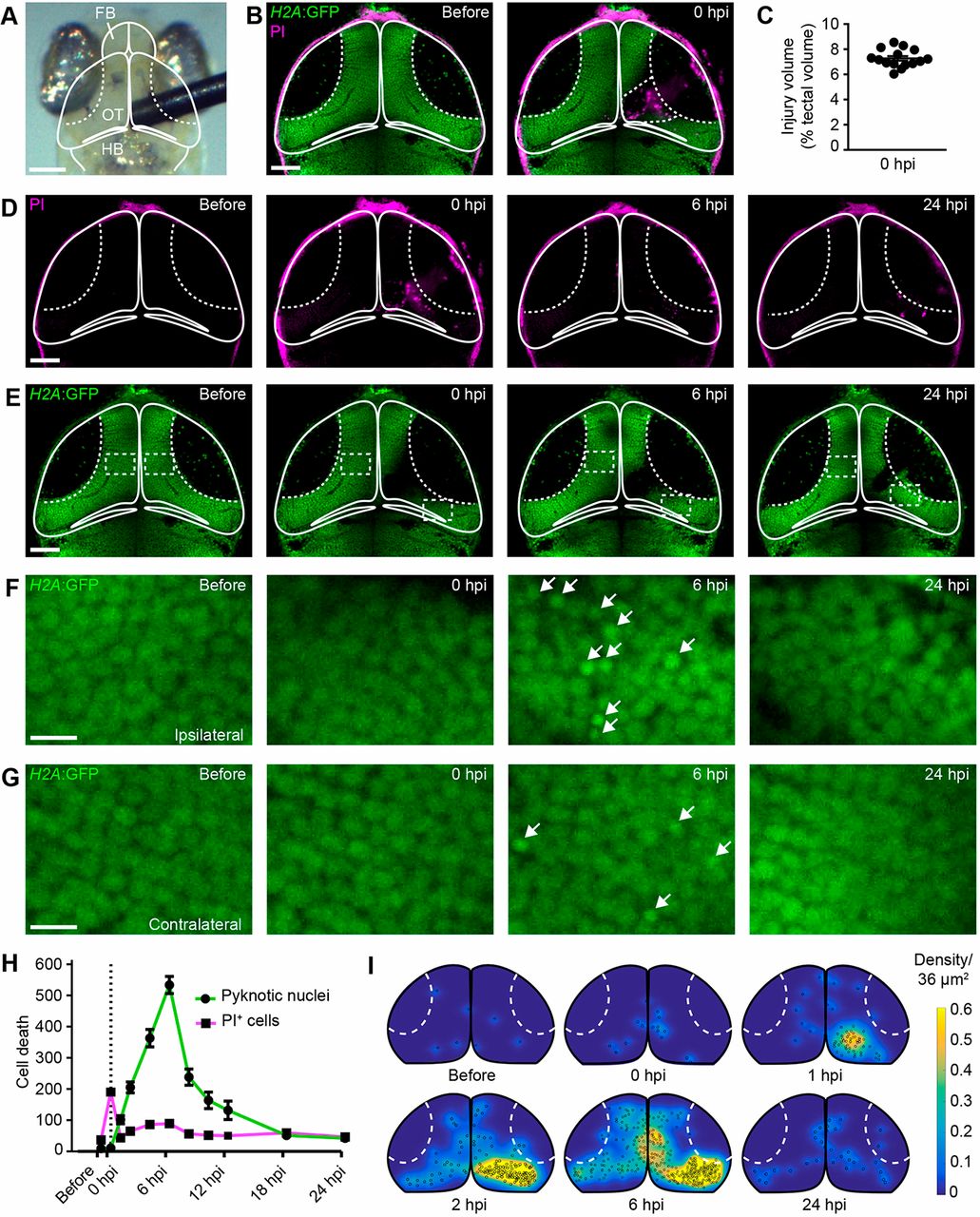
Mechanical injury induces two distinct phases of cell death in the optic tectum of larval zebrafish. (A) Bright-field image of the head of a larval zebrafish. Mechanical brain injury is induced by piercing the optic tectum with a fine metal pin. FB, forebrain; OT, optic tectum; HB, hindbrain. Scale bar: 100?µm. (B) Confocal images of the optic tectum of a H2A:GFP transgenic animal with PI before and immediately after mechanical injury. The damaged area of the cell body layer is outlined. Scale bar: 50?µm. (C) Quantification of injury volume at 0 hpi. n=15 animals. (D,E) Confocal images of PI (D) and H2A:GFP (E) from the animal shown in (B) at different time points after injury. Scale bars: 50?µm. (F,G) Higher magnifications of the boxed regions indicated in E. White arrows indicate pyknotic nuclei. Scale bars: 5?µm. (H) Quantification of PI+ cells and pyknotic nuclei over time after mechanical injury. Dashed line indicates time of injury. n≥9 animals per experimental group. (I) Heat maps illustrating the spatial distribution of pyknotic nuclei in H2A:GFP animals in the hours following injury.