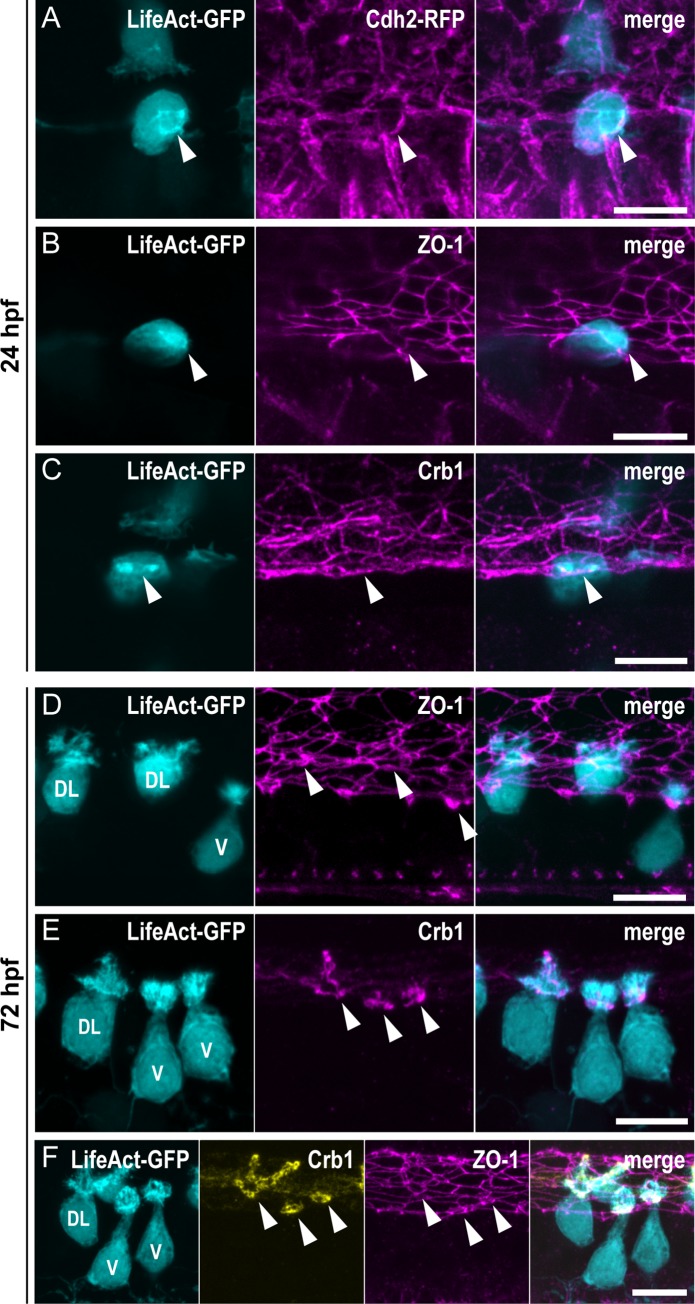
Fig 2
(A–C) Z-projections from lateral views of the spinal cord in 24-hpf embryos showing the colocalization of the ring of actin (LifeAct; arrowheads) with different markers of the AJCs: (A) Cdh2 for adherens junctions, (B) ZO-1 for tight junctions, and (C) Crb1 for the apical domain. (A) Double immunostaining for GFP and RFP in triple transgenic