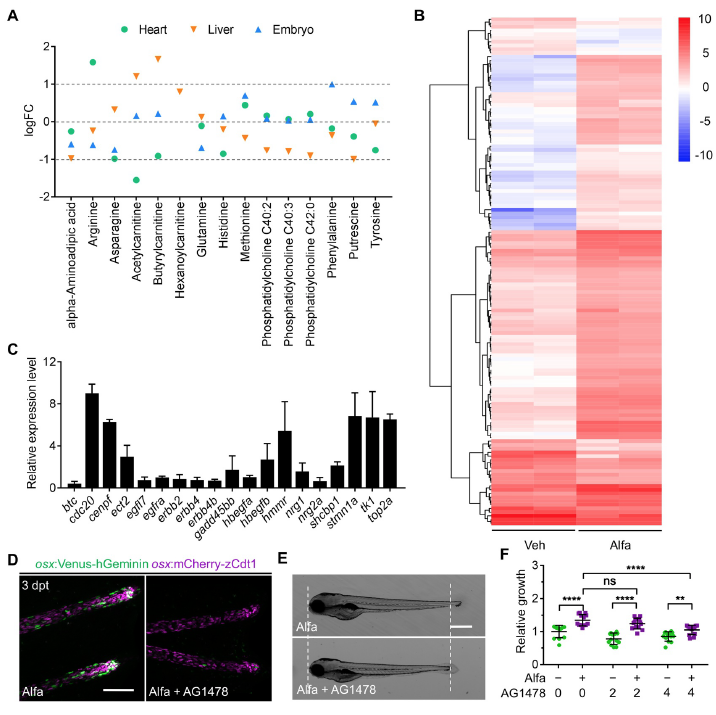
Fig. S4
Vitamin D-Regulated Proliferation and Growth Require ErbB2 Signaling
(Related to Figure 4)
(A) Metabolomic analysis indicating metabolites in heart, liver, or whole-embryo that
were significantly changed by alfacalcidol treatment. Only the metabolites showing
statistically different levels in at least one tissue type are shown.
(B) Heat map of the relative expression levels of the differentially expressed genes that
are predicted to be regulated by ErbB2 signaling pathway using IPA software.
(C) Quantitative RT-PCR of selected ErbB2/ErbB4 ligands (tan), receptors (light blue)
and target genes (gray) in Alfa-injected hearts over control hearts. Data are shown as
relative expression from two biological repeats. eef1a1l1 was used as internal control.
(D) Representative maximum projection images of osx:Venus-hGeminin; osx:mCherryzCdt1
(FUCCI) caudal fin rays from Alfa-injected zebrafish treated with vehicle or
AG1478 for 24 hours starting at 2 hours after the last Alfa injection. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(E) Lateral view of 4 dpf embryos treated with Alfa or Alfa + AG1478 for 24 hours. Scale
bar, 500 μm.
(F) Quantification of lengths of 4 dpf embryos treated with vehicle, Alfa, AG1478 or Alfa
+ AG1478 at the indicated concentrations (μM) for 24 hours. n = 13 for all groups. ns,
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 48(6), Han, Y., Chen, A., Umansky, K.B., Oonk, K.A., Choi, W.Y., Dickson, A.L., Ou, J., Cigliola, V., Yifa, O., Cao, J., Tornini, V.A., Cox, B.D., Tzahor, E., Poss, K.D., Vitamin D Stimulates Cardiomyocyte Proliferation and Controls Organ Size and Regeneration in Zebrafish, 853-863.e5, Copyright (2019) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell