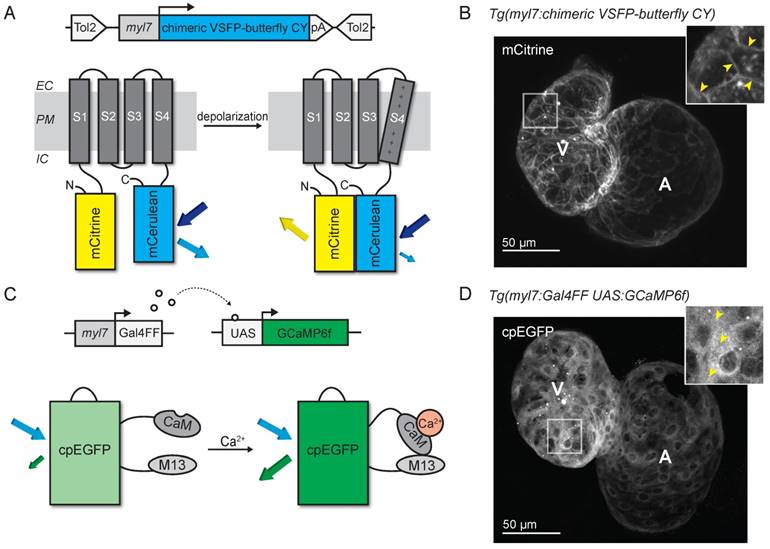
Fig. 1
Development of voltage- and Ca2+-reporting zebrafish lines. (A) DNA construct and concept of the sensing mechanism of chimeric VSFP-butterfly CY. Chimeric VSFP-butterfly CY was placed under control of the myl7 promoter to restrict its expression to the heart. The sensor consists of a voltage sensitive domain with transmembrane segments S1-S4, sandwiched between a fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) pair of the fluorescent proteins mCitrine and mCerulean. Movement of S4 upon membrane depolarization translates into a change of FRET efficiency. (B) 3D projection of a confocal image of a 3 dpf zebrafish tg(myl7:chimeric VSFP-butterfly CY) heart. Only the mCitrine channel is displayed. Insert shows a magnification of the selected ventricular area; arrowheads highlight the membrane targeting of chimeric VSFP-butterfly CY. (C) DNA construct and sensor dynamics of GCaMP6f. GCaMP6f was placed under the control of the myl7 promoter to restrict its expression to the heart. The Gal4FF-UAS system amplifies its expression. GCaMP6f consists of a circularly permutated enhanced green fluorescence protein (cpEGFP) fused to calmodulin (CaM) and the M13 peptide. When intracellular Ca2+ rises, CaM binds to M13, causing increased brightness of cpEGFP. (D) 3D projection of a confocal image of a 3dpf zebrafish tg(myl7:Gal4FF;UAS:GCaMP6f) heart. Insert shows a magnification of the selected ventricular area; arrowheads highlight cytosolic expression of GCaMP6f. CaM: calmodulin; EC: extracellular; IC: intracellular; pA: poly(A); PM: plasma membrane; tg: transgenic; UAS: upstream activation sequence.