Fig. 6
Fig. 6
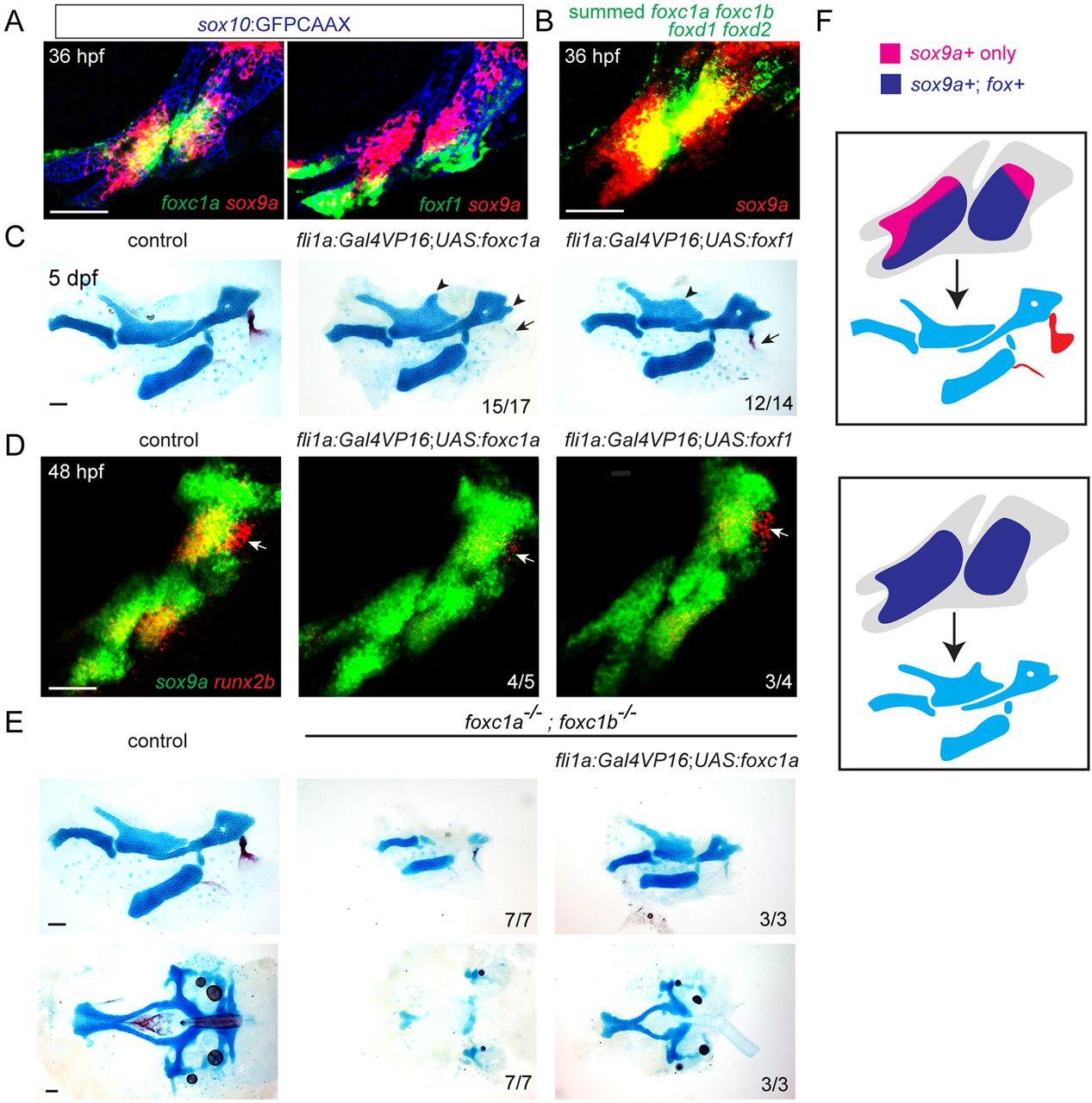
Fox CNC misexpression induces ectopic cartilage and inhibits dermal bone. (A) Confocal sections show expression of foxc1a or foxf1 (green) relative to sox9a (red) in sox10:GFPCAAX+ CNCs of the first two arches (anti-GFP, blue). (B) Maximum intensity projection shows fluorescence in situ hybridization using pooled probes against foxc1a, foxc1b, foxd1 and foxd2 (green) relative to sox9a (red). (C) Unilateral dissections of the first and second arch skeletons stained for cartilage (Alcian Blue) and bone (Alizarin Red). CNC misexpression of Foxc1a (fli1a:Gal4VP16; UAS:foxc1a) or Foxf1 (fli1a:Gal4VP16; UAS:foxf1) results in ectopic cartilage in the upper face (arrowheads), and loss of the opercle bone (arrows). (D) Double fluorescence in situ hybridizations of the first two arches show reduction of the osteoblast gene runx2b (red) in the future opercle bone (arrow) but no change in sox9a (green) upon misexpression of Foxc1a or Foxf1. (E) Dissections of the first and second arch skeletons and neurocranial cartilages. Misexpression of Foxc1a in CNCs (fli1a:Gal4VP16; UAS:foxc1a) rescues cartilage development in the upper face (top) and neurocranium (bottom). Scale bars: 50??m. (F) Model of how arch-wide Fox misexpression expands the territory in which Sox9a induces cartilage (blue) at the expense of dermal bone (red).