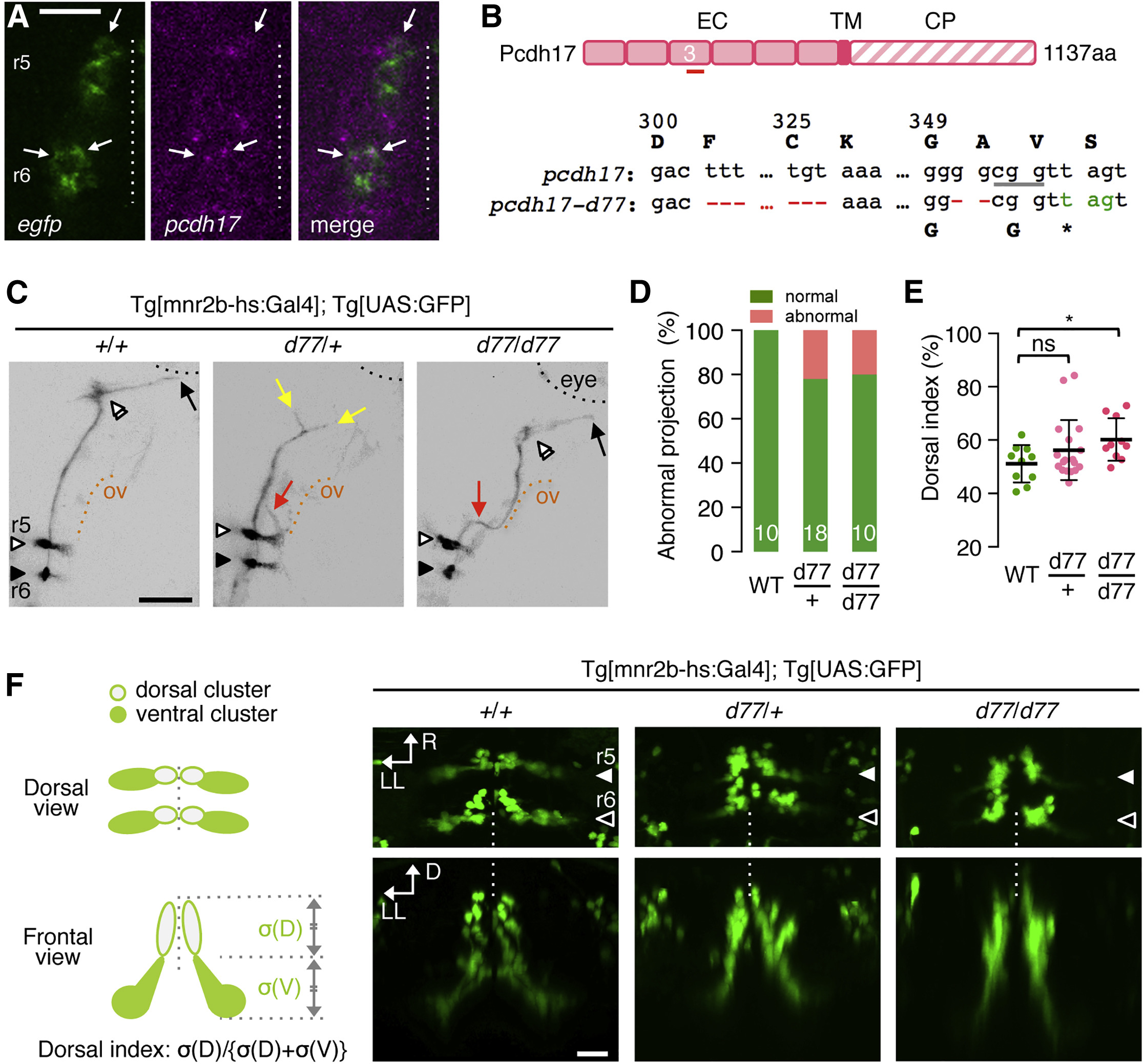
Fig. 5
pcdh17-d77 Mutation Causes Defective Axon Growth and Guidance, as Well as Soma Topography Formation
(A) Fluorescence in situ hybridization for EGFP and pcdh17 in the left hemisegments of r5 and r6 of the Tg[mnr2b-hs:Gal4]; Tg[UAS:GFP] larva at 40 hpf. Arrows indicate stronger pcdh17 signal overlapping EGFP signal.
(B) The pcdh17-d77 allele contains two deletions (red) in the extracellular domain 3 (EC3) generating a premature stop codon (green). The underlined cgg indicates the protospacer adjacent motif (PAM). EC, TM, and CP stand for extracellular, transmembrane, and cytoplasmic domains, respectively.
(C) The axon growth (yellow) and pathfinding (red) defects of mnr2b-ABNs at 3 dpf. The black and orange dashed lines demarcate the eye and otic vesicle (ov), respectively.
(D) Frequency of abnormal axonal projection in wild-type (WT), heterozygous (d77/+), and homozygous (d77/d77) mutant larvae.
(E) Dorsal shift of mnr2b-ABN somata by pcdh17-d77 mutation. The dorsal index is defined by the ratio of the soma areas in the dorsal half of the nucleus (?[D]) to those of all mnr2b-ABNs (?[D] + ?[V]) in a rostrocaudally projected image. ns, p = 0.15; ?p = 0.0144 (unpaired t test). Error bars represent SD.
(F) Nuclear organization mnr2b-ABNs (left) and dorsal and frontal views of mnr2b-ABN somata at 3 dpf.
Scale bars indicate 20 ?m in (A) and (F) and 50 ?m in (C).