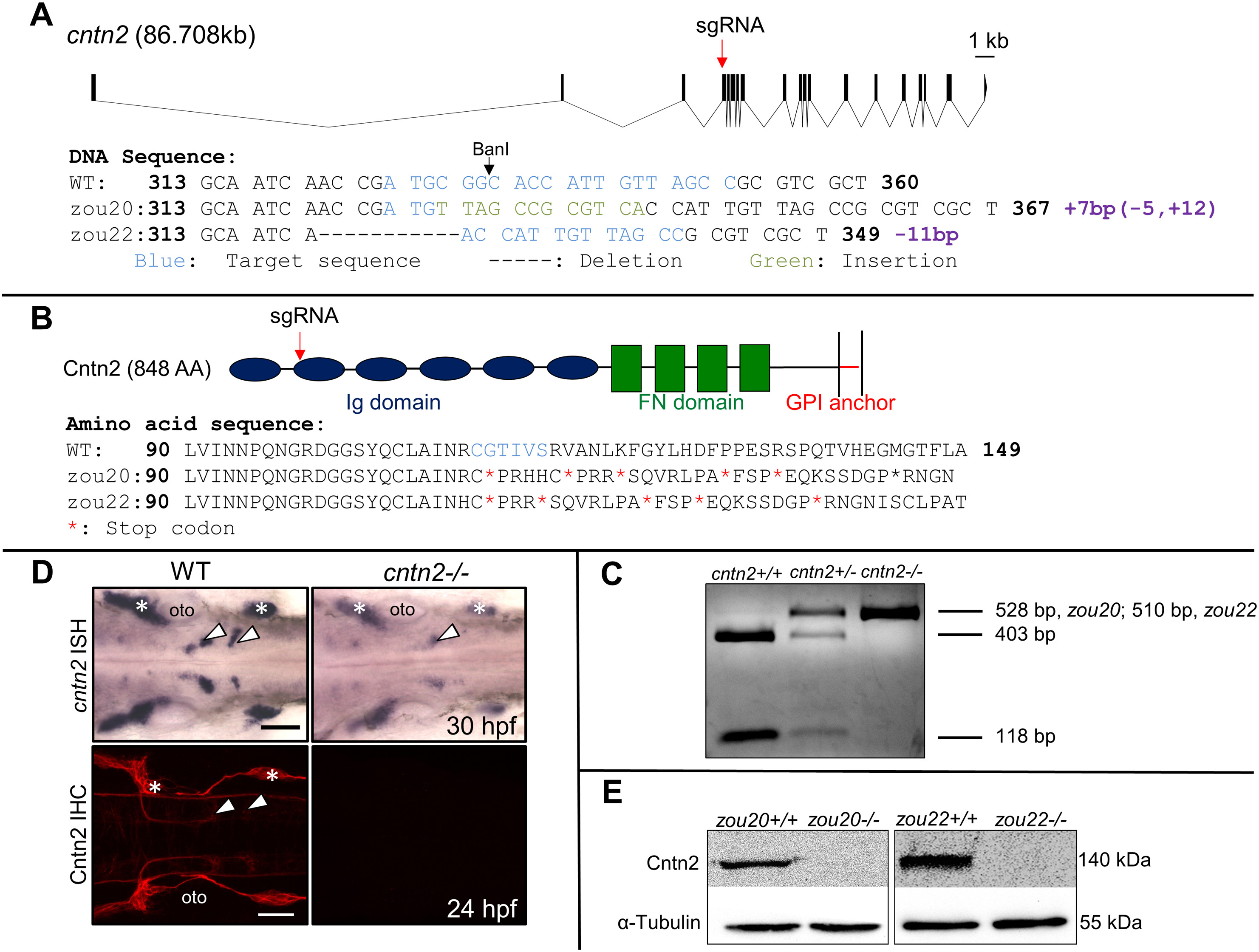
Fig. 1
Generation and validation of CRISPR-generated cntn2 mutant.
(A) Genomic structure of cntn2 containing 19 exons, with the CRISPR target site (sgRNA) in the 4th exon. The target site is highlighted in blue while the 7?bp insertion and the 11?bp deletion in cntn2zou20 and cntn2zou22 alleles are highlighted in green and indicated by dash marks, respectively. (B) Domain structure of Cntn2 containing six immunoglobulin (Ig) domains, four fibronectin (FN) domains, and a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor linked to the plasma membrane. Predicted amino acid sequences of wildtype (WT) cntn2, and cntn2zou20 and cntnzou22 alleles containing multiple stop codons (*). The highlighted AAs (blue) correspond to the CRISPR target site in the gene. (C) A PCR product (528?bp, zou20; 510?bp, zou22) spanning the target site digested with BanI differentiate between three genotypes: Wildtype (2 cut bands), heterozygote (1 uncut and 2 cut bands) and homozygote (1 uncut band). (D) Dorsal views of wildtype (WT) and mutant (zou20) hindbrains processed for cntn2 in situ hybridization (ISH) (upper panels) and anti-Cntn2 immunohistochemistry (IHC) (lower panels). Arrowheads indicate migrated FBM neurons and asterisks mark sensory ganglia. In cntn2 (zou20) mutants, cntn2 expression is greatly reduced, and Cntn2 protein is not detectable. Scale bar?=?50??m. (E) Western blot analysis of Cntn2 in cntn2zou20 and cntnzou22 embryos at 48 hpf. Cntn2 protein is not detectable in cntn2 mutants. Loading control is ?-tubulin. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 152, Gurung, S., Asante, E., Hummel, D., Williams, A., Feldman-Schultz, O., Halloran, M.C., Sittaramane, V., Chandrasekhar, A., Distinct roles for the cell adhesion molecule Contactin2 in the development and function of neural circuits in zebrafish, 1-12, Copyright (2018) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.