Fig. S2
Impaired differentiation in Ddx27 deficiency.
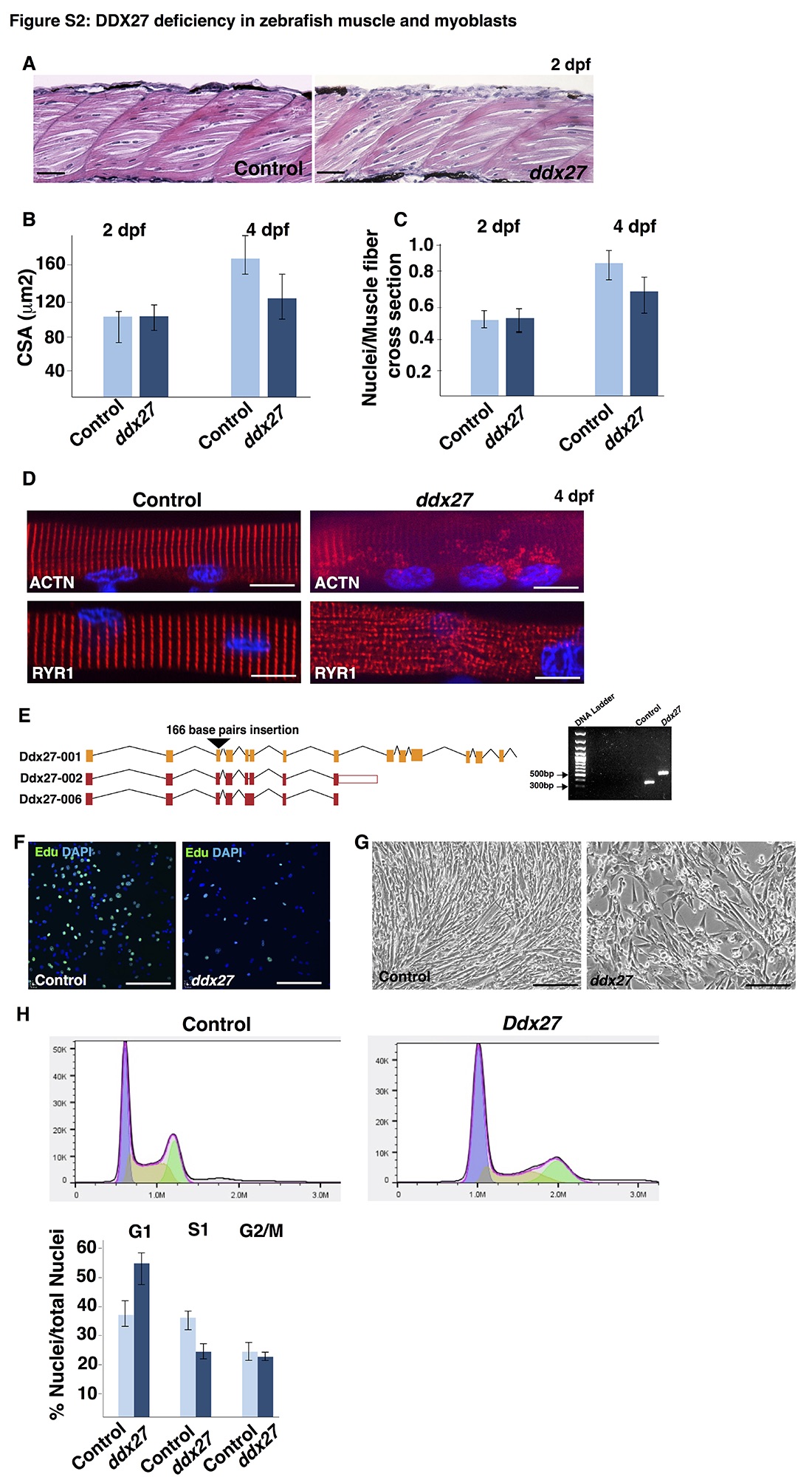
(A) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of embryonic skeletal muscle (2dpf) in control and ddx27 zebrafish.
(B) Skeletal muscle growth during embryogenesis (2 dpf) and larval stages (4 dpf) was assessed by measuring cross-section area of myofibers in control and mutant fish.
(C) Myonuclear content in control and ddx27 mutant fish was evaluated by quantifying the number of nuclei/myofiber in muscle cross-sections. 5 different areas in myotome were analyzed (n = 4).
(D) Control and ddx27 zebrafish myofibers (4 dpf) were cultured and immunofluorescence analysis was performed. Expression of sarcomeric ?-actinin labeling Z-line was reduced in mutant myofibers. Expression of sarcoplasmic reticulum marker, Ryr1 showed a disorganized pattern in comparison to control myofibers (scale bar: 100?m).
(E) Three different guide RNAs (sgRNA) were designed targeting mouse Ddx27 gene. sgRNA targeted to exon3 of all three Ddx27 transcripts resulted in a 166 base pair homozygous insertion and generation of several stop codons. PCR analysis of genomic DNA revealed an insertion in exon3 of Ddx27 gene.
(F) Control and Ddx27 mutant C2C12 were plated at equal concentration and grown in the proliferation media. Cells were pulsed treated with Edu (FITC signal) and counterstained with DAPI.
(G) Control and Ddx27 mutant C2C12 cells were plated at equal cell density and grown in the differentiation media for 7 days. Control cells differentiated in to well differentiated myotubes/myofibers whereas Ddx27 cells exhibited a severe differentiation defects (scale bar: 50?m).
(H) Cell cycle analysis in control and Ddx27 myoblasts.