Fig. 1
ALPK2 Identification and Expression Analyses
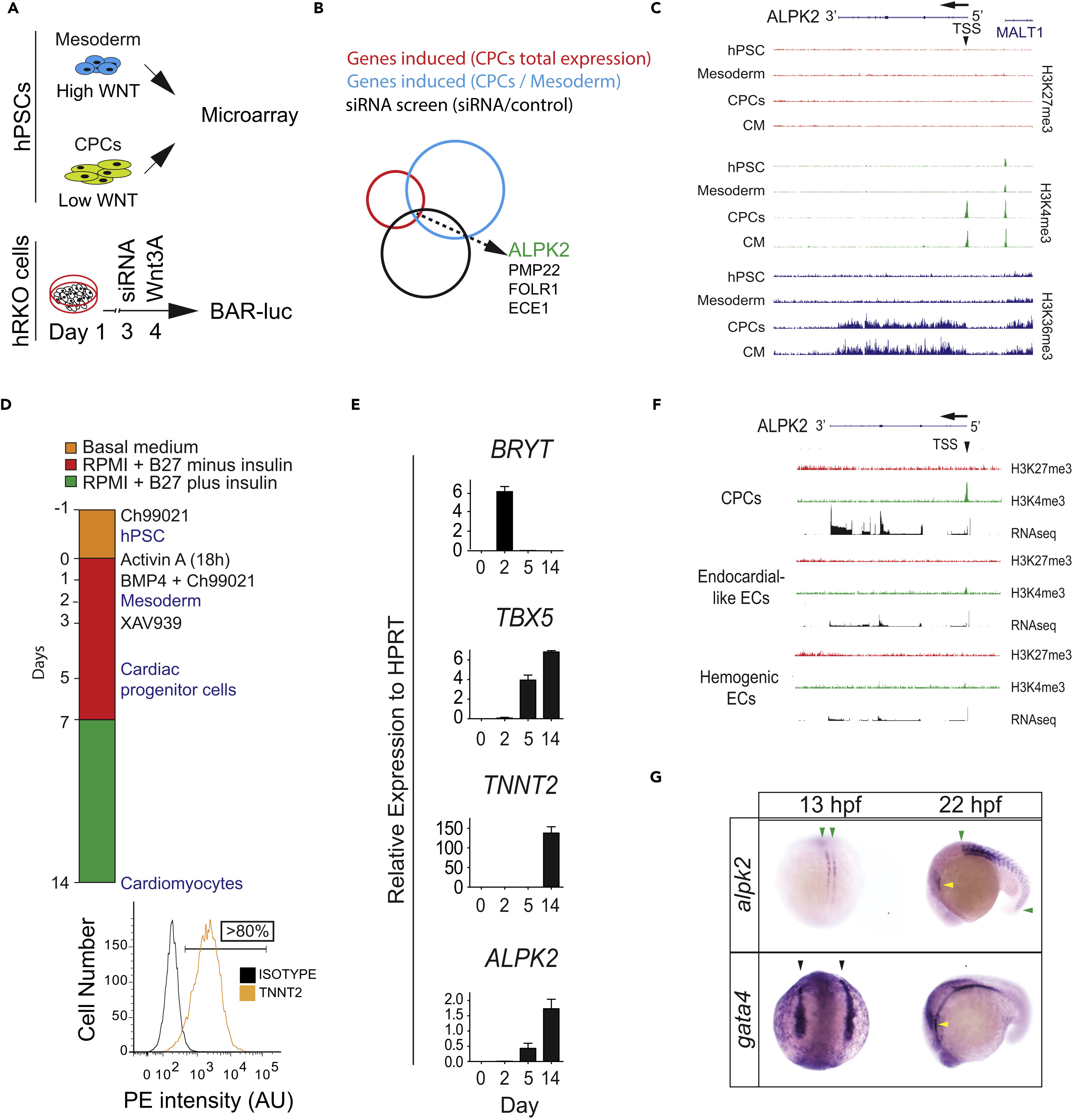
(A) Schematic of combinatorial screening of RNA expression from hESC cardiomyocyte differentiation from human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) coupled with an siRNA screen using ?-catenin-activated reporter (BAR)-transduced human RKO colon carcinoma cells (hRKO) stimulated with recombinant Wnt3A.
(B) Venn diagram identifying Alpha Protein Kinase 2 (ALPK2).
(C) Chromatin precipitation followed by deep sequencing (ChIP-Seq) for histone marks H3K4me3, H3K36me3, and H27K4me3 in hESC-derived cultures: hESC (day 0), mesoderm (day 2), cardiac progenitor cells (CPCs, day 5), and cardiomyocytes (day 14) (N = 2).
(D) Protocol for high-density monolayer-directed differentiation of hESC-derived cardiomyocytes yielding a high percentage of cardiac troponin T (TNNT2)-positive cells by flow cytometry.
(E) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of markers of mesoderm (Brachyury T, BRYT), cardiac progenitor cells (T-box 5, TBX5), cardiomyocytes (TNNT2), and ALPK2 at days 0, 2, 5, 14 during cardiomyocyte differentiation.
(F) RNA sequencing and ChIP-seq for H3K4me3 and H27K4me3 at the ALPK2 locus in CPCs, endocardial-like endothelial cells (EC), and hemogenic ECs (N = 2).
(G) In situ hybridization of zebrafish alpk2 and gata4 at 13 hpf and 22 hr post fertilization (hpf, N = 22?36). Green arrowheads denote adaxial cells and primitive somites, black arrowheads mark the bilateral heart fields, and yellow arrowheads denote the primitive heart. Sample size N = 3?5 biological replicates, and data are displayed as mean ± SEM unless otherwise noted. See also Figure S1.