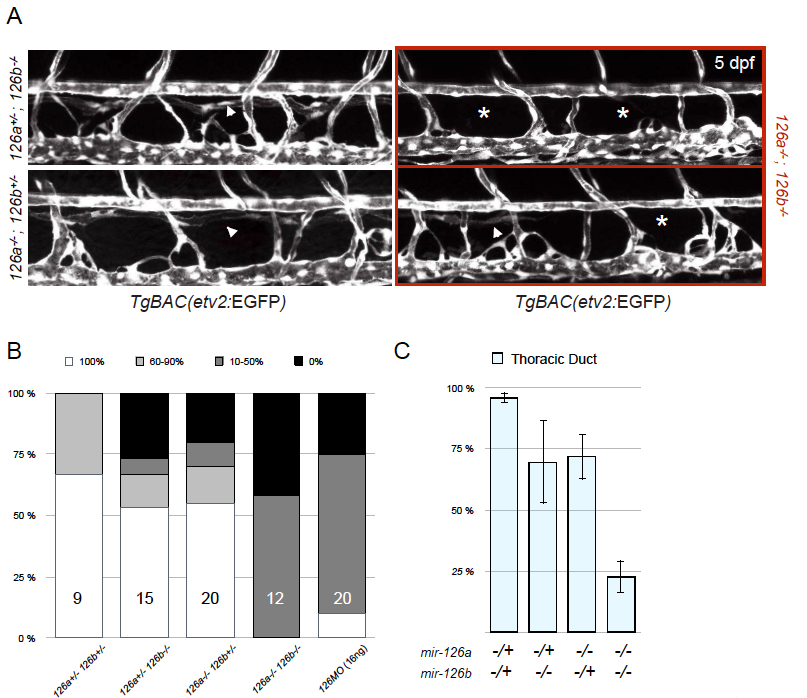
Fig. S6
Penetrance of the thoracic duct phenotype in mir-126a and mir-126b mutants. (A) Confocal images of TD formation in mir-126a-/-; mir-126b+/-, mir-126a+/-; mir-126b-/-, and mir-126a-/-; mir-126b-/- larvae at 5 dpf. (B) Larvae were put into 4 categories according to TD formation (100%, 60?90%, 10?50%, and 0%). Double heterozygous larvae (mir-126a+/-; mir-126b+/-) show minimal TD defects. As more mir-126 alleles are ?lost?, the penetrance of the phenotype increases. mir-126 morphants (16?ng) exhibit a similar penetrance as mir-126 mutants do. n, number of larvae for this particular experiment are indicated in the bars. (C) Plotting the average TD formation per genotype group shows that the phenotype is strong in the mir-126 population. Error bars are showing SEM. Graph shows data from one representative experiment. Analyses were done>?3 times and were consistent across all.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 437(2), Kontarakis, Z., Rossi, A., Ramas, S., Dellinger, M.T., Stainier, D.Y.R., Mir-126 is a conserved modulator of lymphatic development, 120-130, Copyright (2018) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.