Fig. 10
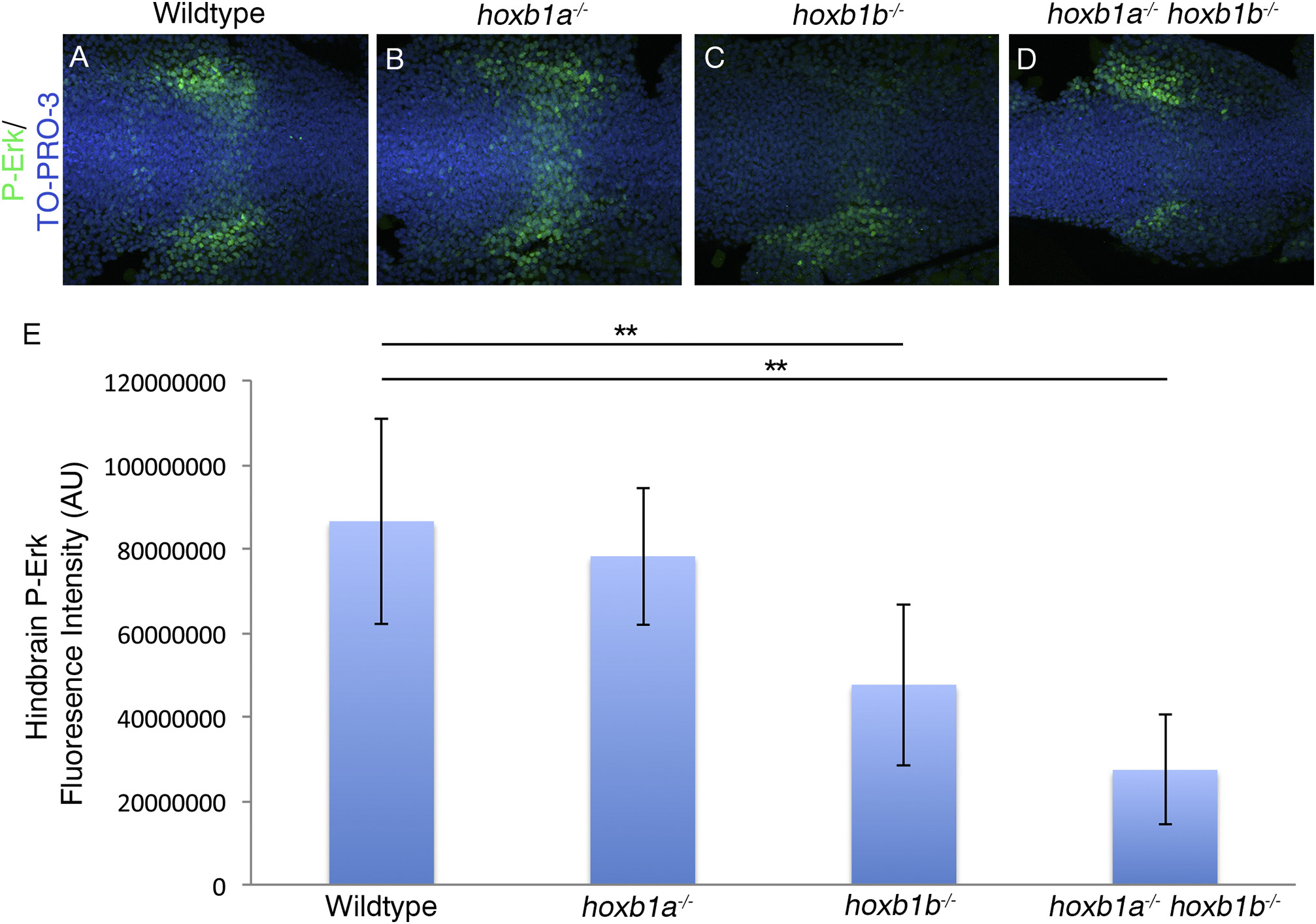
Hoxb1b regulation of FGF signaling results in decreased P-Erk localization.
P-Erk is localized across the hindbrain in presumptive r4 and in lateral wings adjacent to the hindbrain in wildtype and hoxb1a?/? mutants (A-B). In hoxb1b?/? mutants (20/25 embryos)(C) and hoxb1a?/?hoxb1b?/? mutants (9/9 embryos)(D) P-Erk localization in the r4 domain across the hindbrain is reduced. Fluorescence intensity in the hindbrain was quantified using Image J, and the average fluorescence intensity was calculated (E). Hoxb1b?/? mutants have a 45% decrease in intensity while hoxb1a?/?;hoxb1b?/? double mutants have a 68% decrease in intensity. Error bars indicate standard deviation. Wildtype: 86490590AU, hoxb1a?/?: 78175326AU, hoxb1b?/?: 47583826AU, hoxb1a?/?;hoxb1b?/?: 27314030AU (ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey's: Wildtype vs hoxb1b?/?, p-value 0.007; Wildtype vs hoxb1a?/?;hoxb1b?/?, p-value 0.001) All embryos have been genotyped for hoxb1asa1191 and hoxb1bua1006. All images are dorsal views, anterior to the left, 4 somites.
Reprinted from Mechanisms of Development, 150, Selland, L.G., Koch, S., Laraque, M., Waskiewicz, A.J., Coordinate regulation of retinoic acid synthesis by pbx genes and fibroblast growth factor signaling by hoxb1b is required for hindbrain patterning and development, 28-41, Copyright (2018) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Mech. Dev.