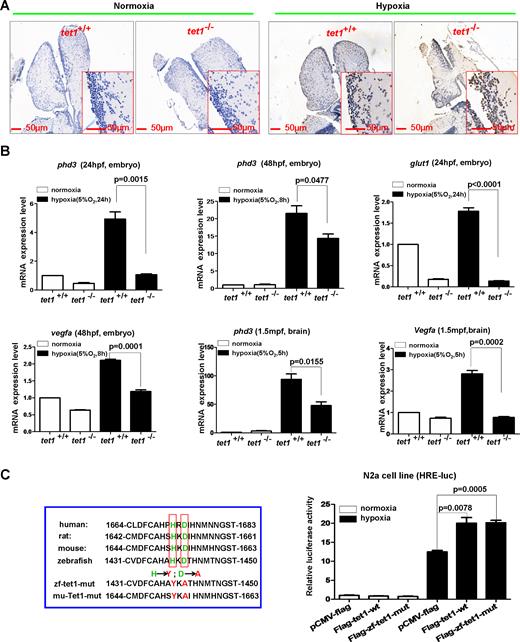
Fig. 2
Knockout of tet1 in zebrafish causes more apoptotic cells in the brain and reduction of hypoxia-inducible gene expression under hypoxia. (A) Compared with those in the brain of wild-type siblings, more apoptotic cells were detected in the brain of tet1-null zebrafish by TUNEL assays under hypoxia (5% O2, 5 h). (B) Expressions of hypoxia-inducible genes including phd3, glut1, vegfa were reduced significantly in the brain of tet1-null zebrafish embryos and adults compared with those of their wild-type siblings under hypoxia. (C) Overexpression of both zebrafish tet1 and its enzymatic inactive form (zf-tet1-mut) could activate the hypoxia response element luciferase (HRE-luc.) reporter in the N2a cell line under hypoxia. N2a cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and luciferase activity was measured 20?24 h after transfection. The left red box indicates the alignment of partial Tet1 sequences surrounding Tet1 enzymatic activity region and the enzymatic inactive mutant (mut) with histidine mutated to tyrosine and aspartic acid mutated to alanine. zf-tet1-mut, zebrafish tet1 mutant; mu-Tet1-mut, mouse Tet1 mutant.