Fig. 2 S1
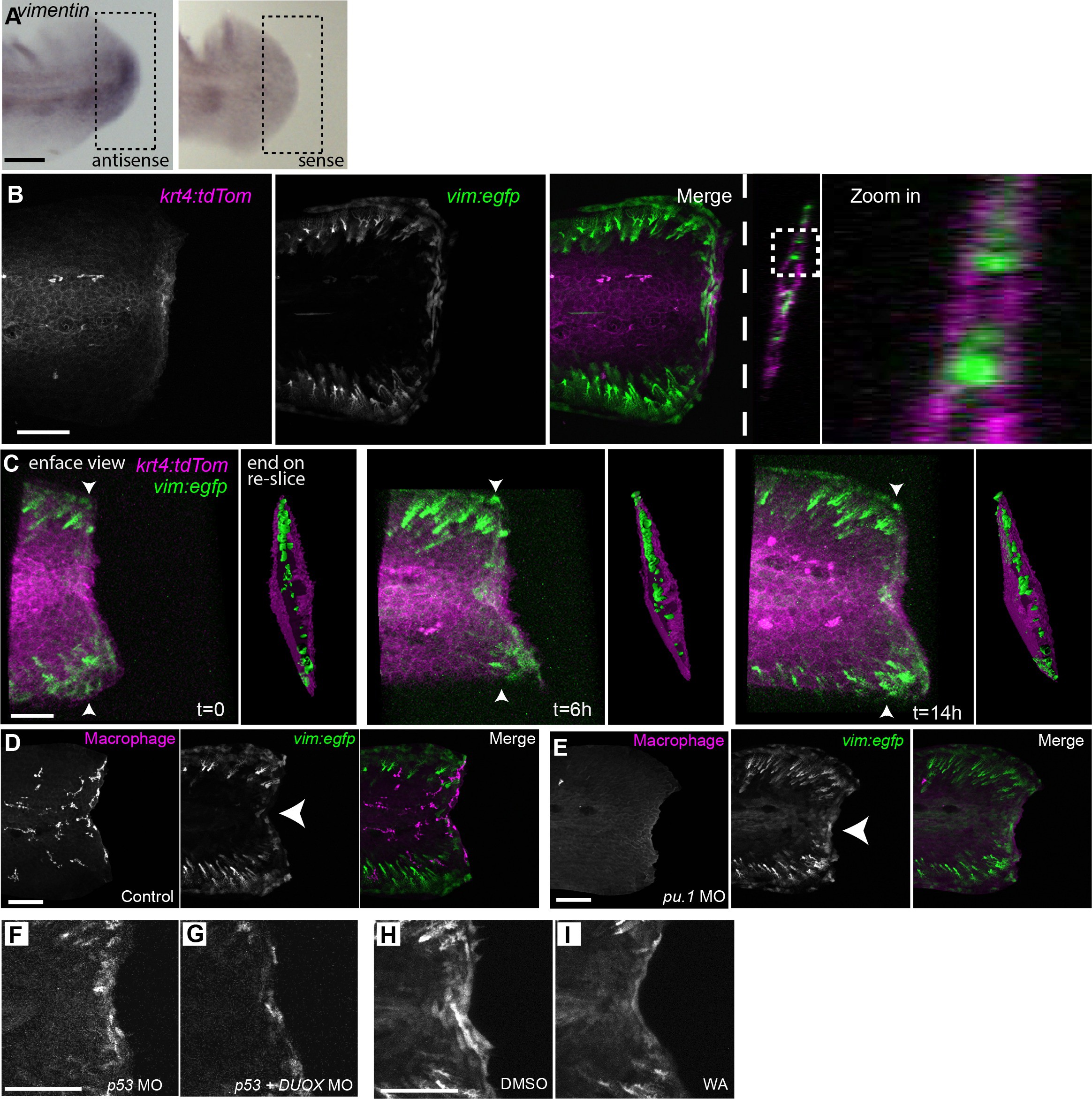
Vimentin expression at the wound edge did not co-localize with epithelial or macrophage markers and was not influenced by leukocyte depletion.
(A) In situ hybridization for vimentin at 24 hpw, showing anti-sense and sense labeling. (B) Vimentin-positive cells did not co-localize with krt4-positive cell populations at the wound edge at 24 hpw as visualized by confocal imaging of larvae by crossing the Tg(?2vim:egfp) and Tg(krt4:tdtom) lines. (C) 3-dimensional reconstructions of 3 time points from time-lapse recording (Figure 2?video 2) of wounded caudal fin from a Tg(?2vim:egfp) and Tg(krt4:tdtom) cross, showing both an enface view and a re-sliced end on view, with the re-slice indicated by arrowheads on enface view, of surface rendered three dimensional reconstructions for each time point, illustrating that gfp expression was not detected co-localizing with the tdTom expression. t = 0 is 12 hpw. (D) EGFP does not co-localize with a macrophage marker and (E) removal of leukocytes by morpholino knockdown of the pu.1 transcription factor did not inhibit the activation of the vimentin promoter at the wound edge at 24 hpw. (F,G) DUOX MO reduced EGFP signal at the wound edge at 24 hpw. (H, I) The activation of the vimentin promoter was regulated by NF?B as treatment with WA reduced EGFP signal at the wound edge at 24 hpw as compared to control DMSO. Scale bars in A, B, D, F and H represent 100 Ám and 50 Ám in C.