Fig. S13
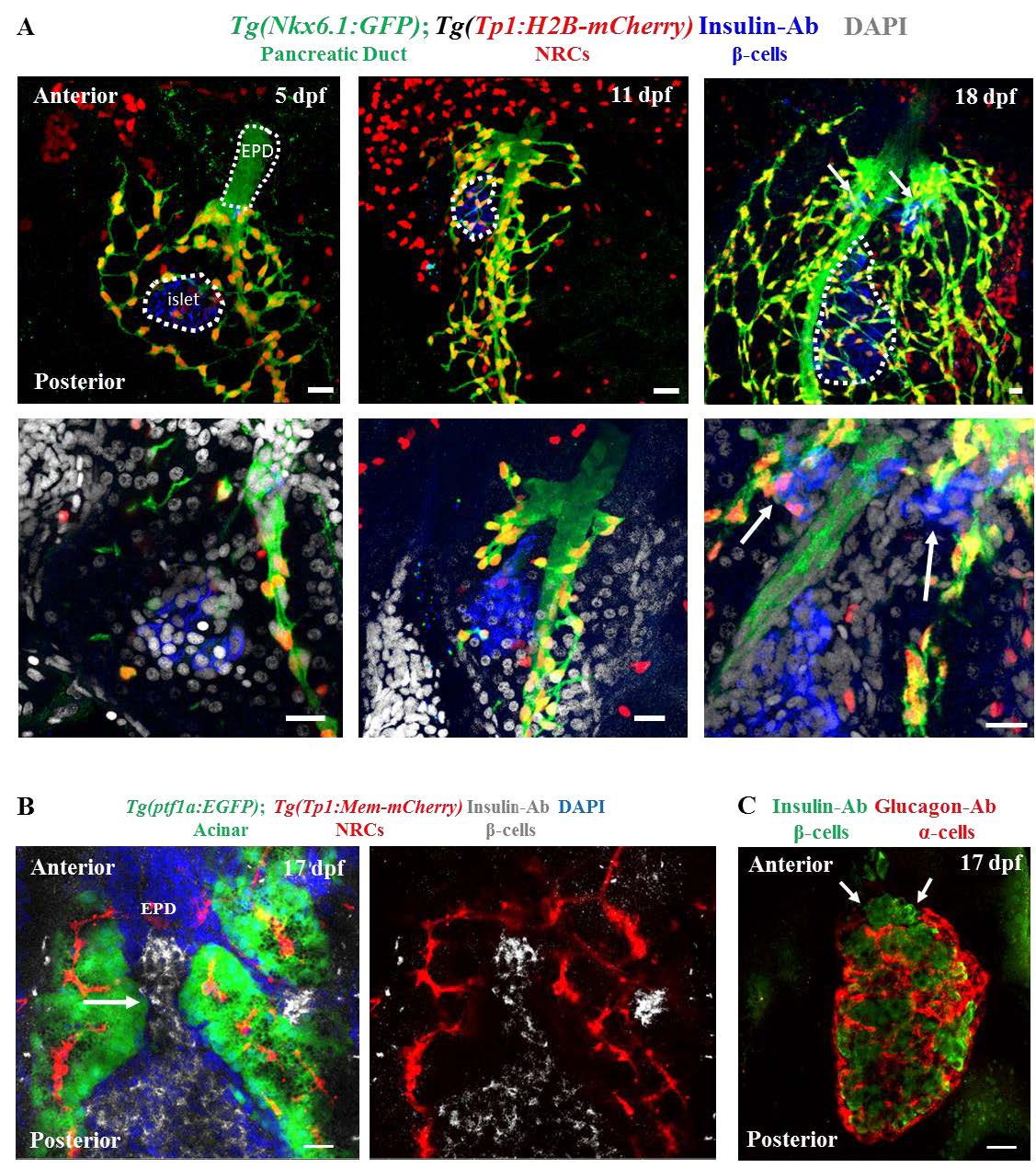
Beta-cells that differentiate from post-embryonic progenitors coalesce with the anterior side of the principal islet. (A) Time course analysis of beta-cells and beta-cell progenitors at 5, 11, and 18 dpf. The progenitor population consists of Notch-responsive cells (NRCs) within the ductal lineage. Tg(Tp1:H2B-mCherry) marks the NRCs (red), while the entire ductal linage exhibits expression of Tg(Nkx6.1:GFP) (green). Insulin immunofluorescence marks the beta-cells. The primary islet is outlined in the maximum intensity projections (top panels). The bottom panels represent single-plane images at higher magnification. Note the lack of NRCs within the extra-pancreatic duct (EPD, outlined at 5 dpf). Arrows at 18 dpf indicate two clusters of beta-cells in proximity to the anterior side of the primary islet. (B) Maximum intensity projection of the pancreata of 17 dpf Tg(ptf1a:EGFP); Tg(Tp1:mem-mCherry) animals stained for insulin and DAPI. Acinar cells were labeled by Tg(ptf1a:EGFP)-expression and NRCs were labeled by Tg(Tp1:mem-mCherry)-expression. A cluster of beta-cells is transitioning between the acinar cells and appears to coalesce with the anterior side of the primary islet (arrow). (C) Maximum intensity projections of the pancreata of 17 dpf animals stained with anti-glucagon and anti-insulin antibodies to mark alpha- and beta-cells, respectively. Alpha-cells form the outer layer of the islet and surround the beta-cells, which are located inside the islet. The anterior side of the islet exhibits an opening within the alpha-cell layer (arrows), which is filled with the beta-cells incorporating into the anterior side of the primary islet. Note that the alpha-cell layer remains un-interrupted along the lateral and posterior sides of the islet. Scale bars, 20 ?m.