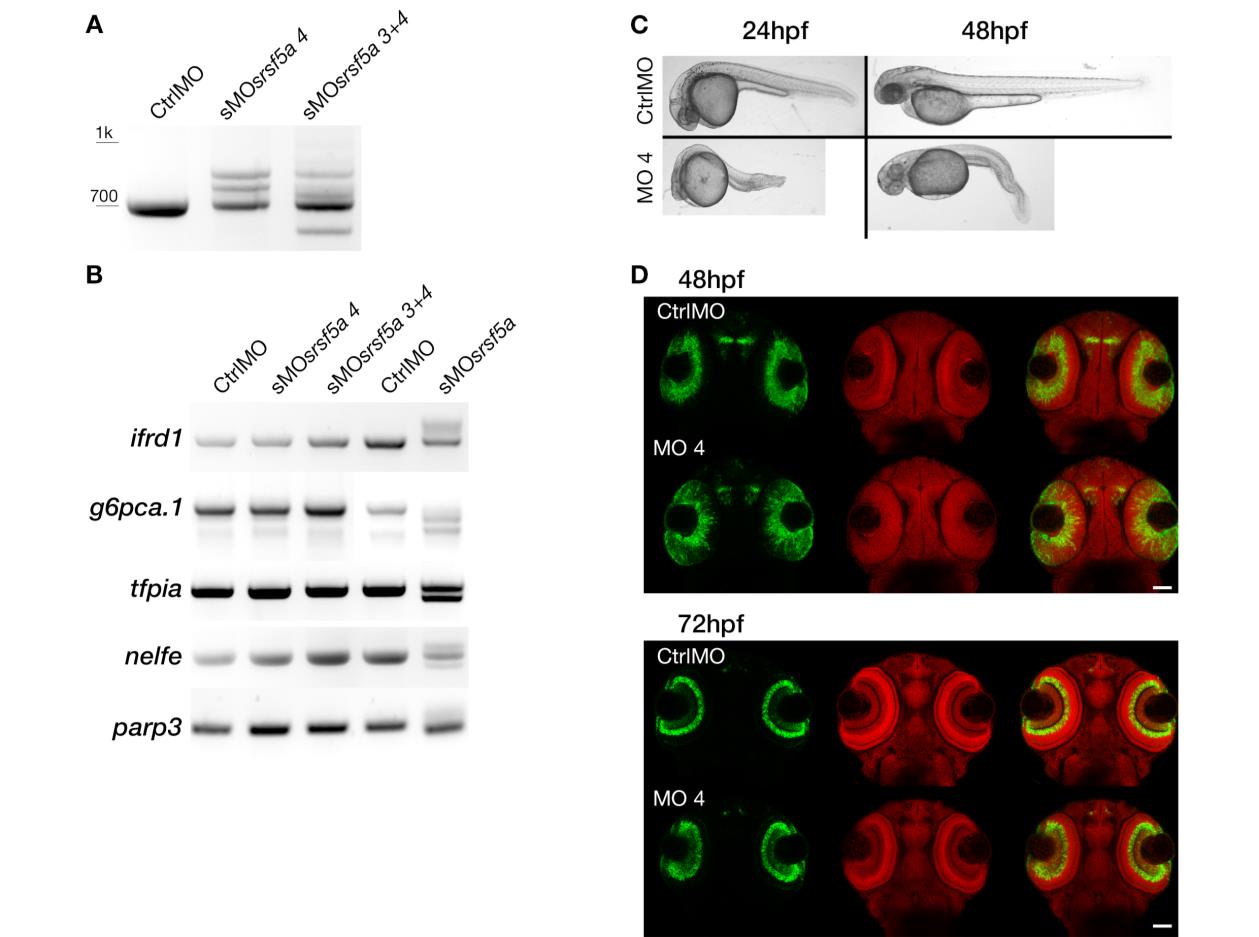
Fig. S4
Microinjection of sMOsrsf5a4 did cause the same phenotype as sMOsrsf5a. A, RT-PCR experiments to amplify srsf5a mRNA in 48 hpf embryos injected with a control morpholino (CtrlMO), 4ng of sMOsrsf5a4 (sMOsrsf5a4) or co-injected with 3ng of sMOsrsf5a3 and sMOsrsf5a4 (sMOsrsf5a3+4) were performed. srsf5a splicing was affected in morphants compared to control as well as the srsf5a wt mRNA level. B, The sMOsrsf5a3 and sMOsrsf5a4 did not have the same effect as the sMOsrsf5a on ifrd1, g6pca.1, tfpia, nelfe and parp3 suggesting that differential splicing observed in sMOsrsf5a morphants is due to morpholino inadvertent binding and not to srsf5a knockdown. C, Injection of 4ng of sMOsrsf5a4 led to a high mortality rate (40% of death embryos at 24hpf, n>450), brain necrosis and tail defects (100% of survivable embryos at 24hpf) at 24 and 48hpf. D, Fluorescent in situ hybridization using a pax6b probe followed by nuclear staining using draq7® in 48 and 72 hpf embryos injected with the CtrlMO or the sMOsrsf5a4. No phenotype could be detected except a slight developmental delay in eye formation.