Fig. S1
Related to Figure 1. Myofibril formation is severely affected in qkia/qkic double mutant embryos.
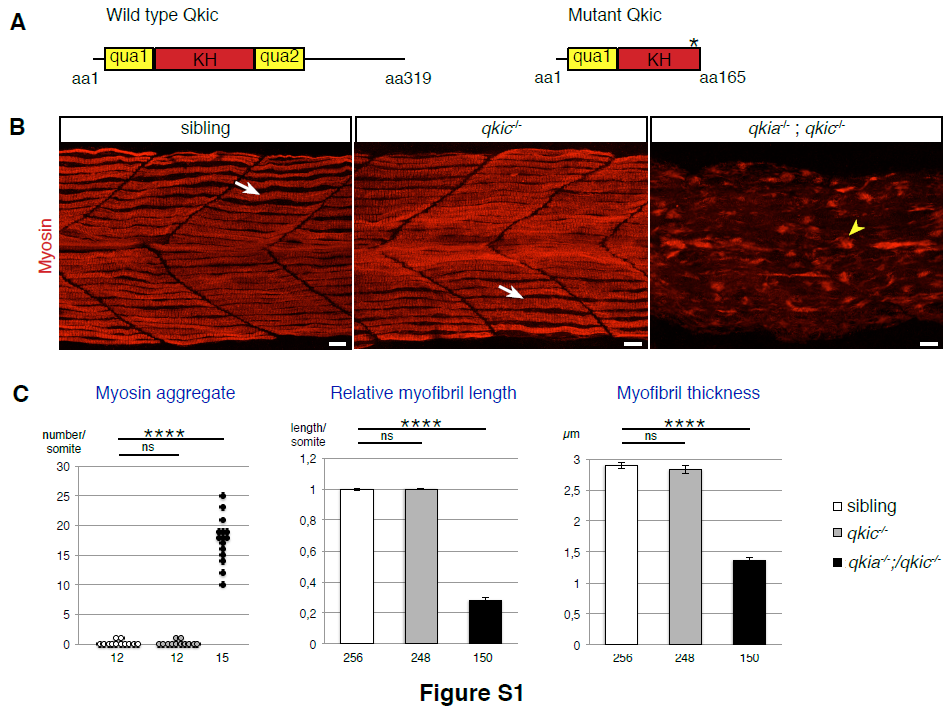
(A) Generation of the qkic mutant allele. Wild-type Qkic protein consists of 319 amino acids (aa) and contains a KH domain flanked by two qua domains, which mediate RNA binding and dimerisation. The qkic mutant allele (qkic463_464insTCAC) generated by the zinc finger technology contains four nucleotides inserted within exon 4. This insertion generates a premature stop codon within the KH RNA binding domain, which is predicted to result in a truncated protein (165aa long) devoid of RNA binding capacity.
(B) Myofibril formation is severely affected in qkia/qkic double mutant embryos, but not in qkic mutant embryos. Confocal imaging with z-projection of myosin-immunostained 26 hpf zebrafish embryos from intercrosses of qkia+/-;qkic+/- parents (lateral view). Similarly to WT, single and double qkia/qkic heterozygous embryos (sibling, n=16), qkic mutant embryos (n=20) exhibit wild-type myofibrils (arrow). In contrast, qkia/qkic double mutant embryos (n=17) display severely affected myofibrils with myosin aggregates (arrowhead).
Anterior is to the left. Scale bar 10μm.
(C) Quantification of the myofibril phenotype illustrated in B. Myofibrils of sibling and qkic-/- embryos are similar (Student’s t-test, P>0.3). In contrast, qkia-/- ; qkic-/- embryos have significantly more myosin aggregate per somite (Student’s t-test, P=5.7x10-11), as well as shorter and thinner myofibrils compared to sibling embryos (Student’s t-test, P=1.6x10-107 and 5.5x10-82 respectively). For each condition, 4 embryos were analysed. Numbers under the graph indicate the total number of quantified somites (left graph) and myofibrils (right and middle graphs). Pooled data are represented as mean +/- SEM.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 42(5), Bonnet, A., Lambert, G., Ernest, S., Dutrieux, F.X., Coulpier, F., Lemoine, S., Lobbardi, R., Rosa, F.M., Quaking RNA-Binding Proteins Control Early Myofibril Formation by Modulating Tropomyosin, 527-541.e4, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell