Fig. 5 S2
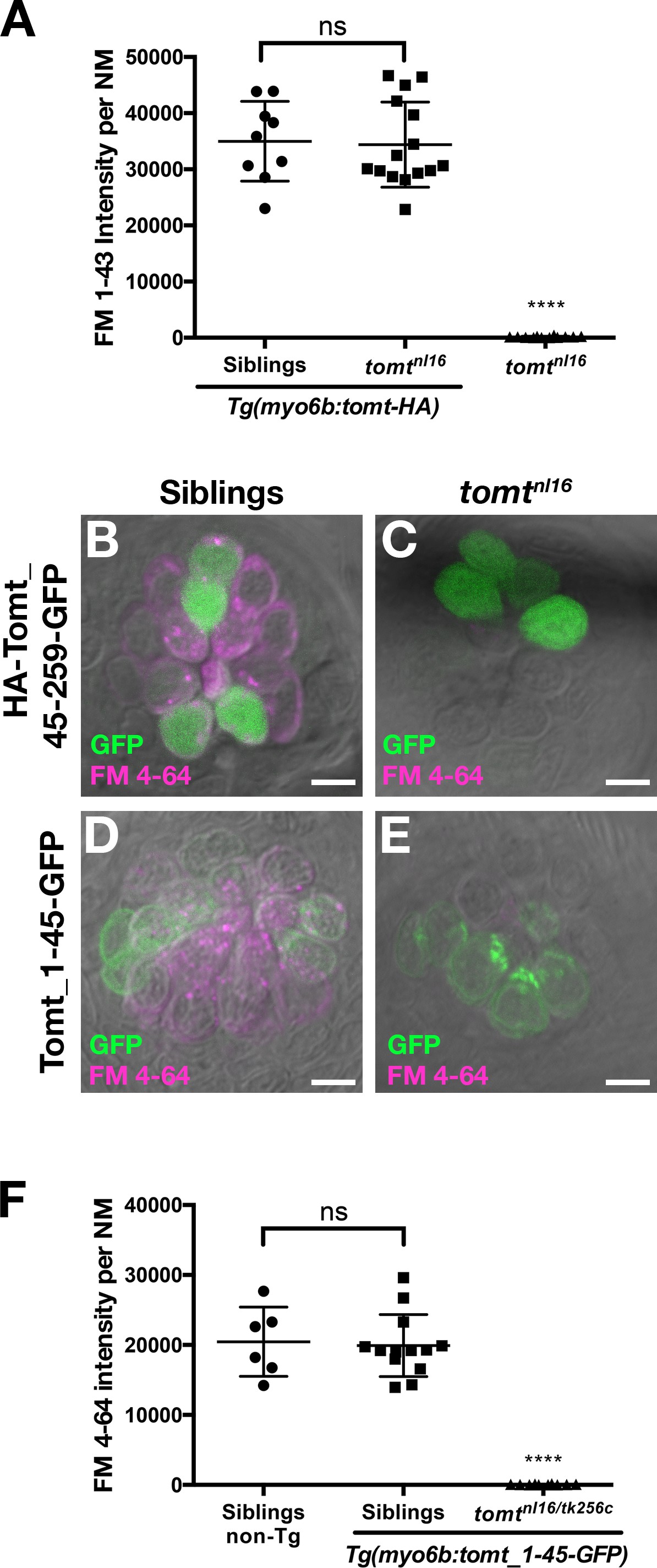
Tomt function requires the putative transmembrane and enzymatic domains.
(A) Tomt-HA can restore basal MET channel activity to mercury mutant hair cells. Quantification of FM 1–43 fluorescence intensity per NM for 5 dpf Tg(myo6b:tomt-HA) siblings (n = 3 larvae, 9 NM) and tomtnl16 mutants (n = 5 larvae, 15 NM), as well as non-transgenic tomtnl16 mutants (n = 4 larvae, 12 NM). Error bars are the mean ± SD. ns = not significant. Asterisks indicate p<0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. (B, C) Representative images of neuromasts from 4 dpf wild-type (B) and tomtnl16 larvae transiently expressing a cytoplasmic form of Tomt (HA-Tomt_45–259-GFP). Cytoplasmic Tomt fails to rescue FM 4–64 label in mercury mutants (n = 7 individuals). (D, E) Representative images of neuromasts from 4 dpf wild-type (B) and tomtnl16 larvae transiently expressing a form of Tomt lacking the putative enzymatic domain (Tomt_1–45-GFP). Transiently expressed Tomt_1–45-GFP fails to rescue FM 4–64 label in mercury mutants (n = 2). (F) Quantification of FM 4–64 fluorescence intensity per NM in 4 dpf stable Tg(myo6b:tomt_1–45-GFP) wild-type siblings (n = 6 larvae, 13 NM) and tomtnl16/tk256c compound mutants (n = 4 larvae, 10 NM), as well as non-transgenic wild-type siblings (n = 2 larvae, 6 NM). Error bars are the mean ± SD. ns = not significant, asterisks indicate p<0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparison test. Scale bars = 5 µm in B-E.