Fig. 2
Inhibition of Mmp2, but Not Mmp9, Function Affects EHT in the VDA
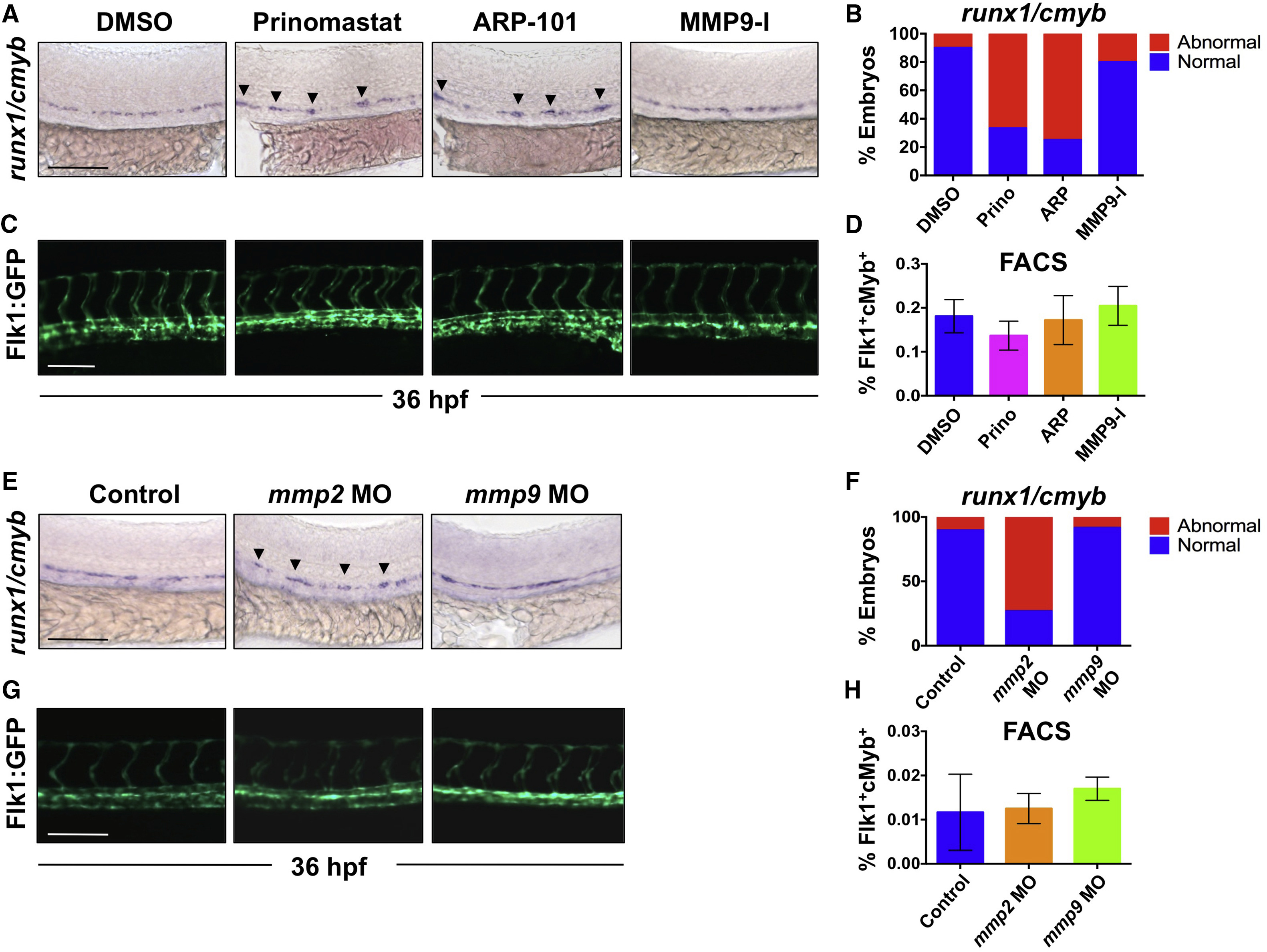
(A) Exposure to prinomastat (20 ?M) or ARP-101 (10 ?M; 12?36 hpf) caused abnormal runx1/cmyb patterning in the VDA, while MMP9-I (5 ?M) had no effect.
(B) Qualitative phenotypic distribution of embryos from (A) scored with normal or abnormal runx1/cmyb expression (n ? 20/condition).
(C) In vivo imaging of Flk1:GFP at 36 hpf indicated that MMP inhibitor (12?36 hpf) treatment did not affect physical vasculature structure (n ? 5 embryos/condition).
(D) FACS analysis of double-positive HSPCs in Tg(kdrl:dsred/cmyb:gfp) embryos showed no difference in HSPCs after MMP inhibitor exposure (12?36 hpf; 5 embryos/sample, ?3 replicates/condition).
(E) MO knockdown of mmp2 or mmp9 phenocopied effects of chemical inhibition on runx1/cmyb WISH at 36 hpf.
(F) Phenotypic distribution of embryos from (E) scored for runx1/cmyb expression (as in A) in the AGM (n value as in B).
(G) MO knockdown of mmp2 or mmp9 had no impact on Flk1:GFP+ endothelium (n value as in C).
(H) FACS analysis of Flk1:dsRed+/cMyb:GFP+ HSPCs showed no significant difference between mmp2 or mmp9 morphants and controls at 36 hpf (n value as in D).
Arrowheads mark HSPC clusters. Error bars denote mean ± SD. Scale bars, 100 ?m.