Fig. 1
Tmem2 Is Required for Angiogenesis and Vegf Signaling
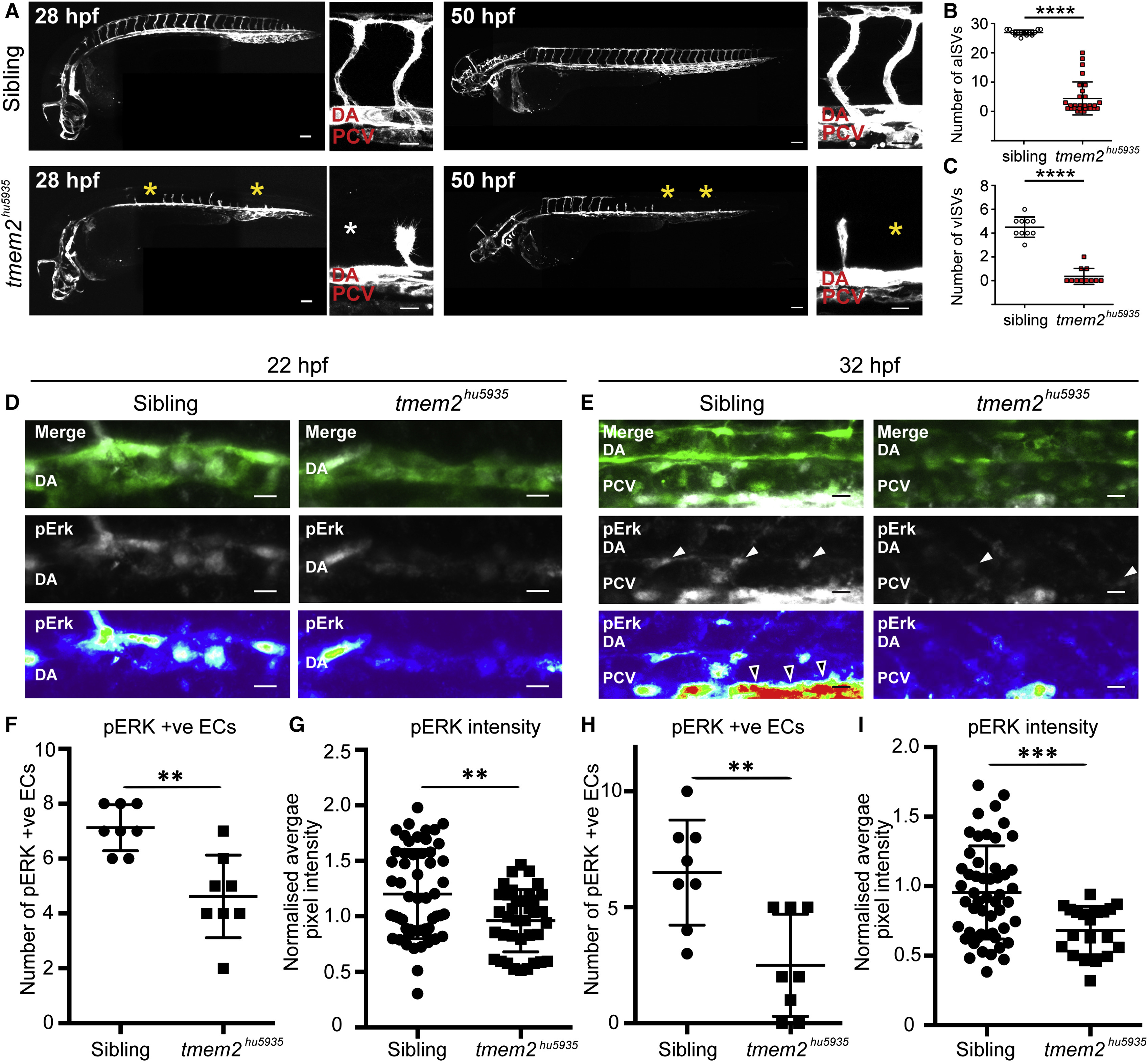
(A) Lateral composite views of sibling and tmem2hu5935 mutant embryos crossed with the Tg(kdrl:mCherry) line (white) show a failure to complete angiogenesis at both arterial (28 hpf) and venous (50 hpf) sprouting stages. Yellow and white asterisks indicate the absence of sprouts in the mutants. Scale bar, 100 ?m for whole embryo and 25 ?m for zoom.
(B) Column scatterplots depicting the number of segments with T-branching arterial ISVs per embryo at 28 hpf (n = 17 siblings, n = 29 mutants).
(C) Scatterplots depicting the number of segments with venous ISVs per embryo at 50 hpf (n = 10 siblings and n = 11 mutants).
(D and E) Maximum projection for whole-mount pErk immunofluorescence staining (white and heatmap) in sibling and tmem2hu5935 mutants on the Tg(kdrl:EGFP) background (green) at (D) 22 hpf and (E) 32 hpf. Average projections of fluorescence intensity for pErk are represented by heatmaps, where blue=low and red=high. Scale bar, 10 ?m. pErk-positive cells indicated with white arrowheads; open arrowheads depict staining in corpuscle of Stannius.
(F and G) Quantification of pErk-positive endothelial cells across four somites showed (F) significantly fewer pErk-positive endothelial cells in tmem2hu5935 mutant embryos compared with siblings at 22 hpf during primary sprouting (n = 8 sibling, n = 8 mutants) and (G) significantly lower fluorescence intensity (normalized to neuronal expression) of pERK-positive endothelial cells in mutants (n = 37) compared with siblings (n = 57) at 22 hpf.
(H and I) Similarly, (H) there were significantly fewer pERK-positive endothelial cells in the PCV across eight somites of mutants (n = 8) at 32 hpf compared with siblings (n = 8; p < 0.01) and (I) significantly lower fluorescence intensity of pERK-positive cells in mutants (n = 20) compared with siblings (n = 52) at 32 hpf.
DA, dorsal aorta; PCV, posterior cardinal vein. ??p < 0.01, ???p < 0.001, ????p < 0.0001. Error bars represent ąSD.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 40, De Angelis, J.E., Lagendijk, A.K., Chen, H., Tromp, A., Bower, N.I., Tunny, K.A., Brooks, A.J., Bakkers, J., Francois, M., Yap, A.S., Simons, C., Wicking, C., Hogan, B.M., Smith, K.A., Tmem2 Regulates Embryonic Vegf Signaling by Controlling Hyaluronic Acid Turnover, 123-136, Copyright (2017) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell