Fig. 3
luc loss-of-function leads to patterning defects.
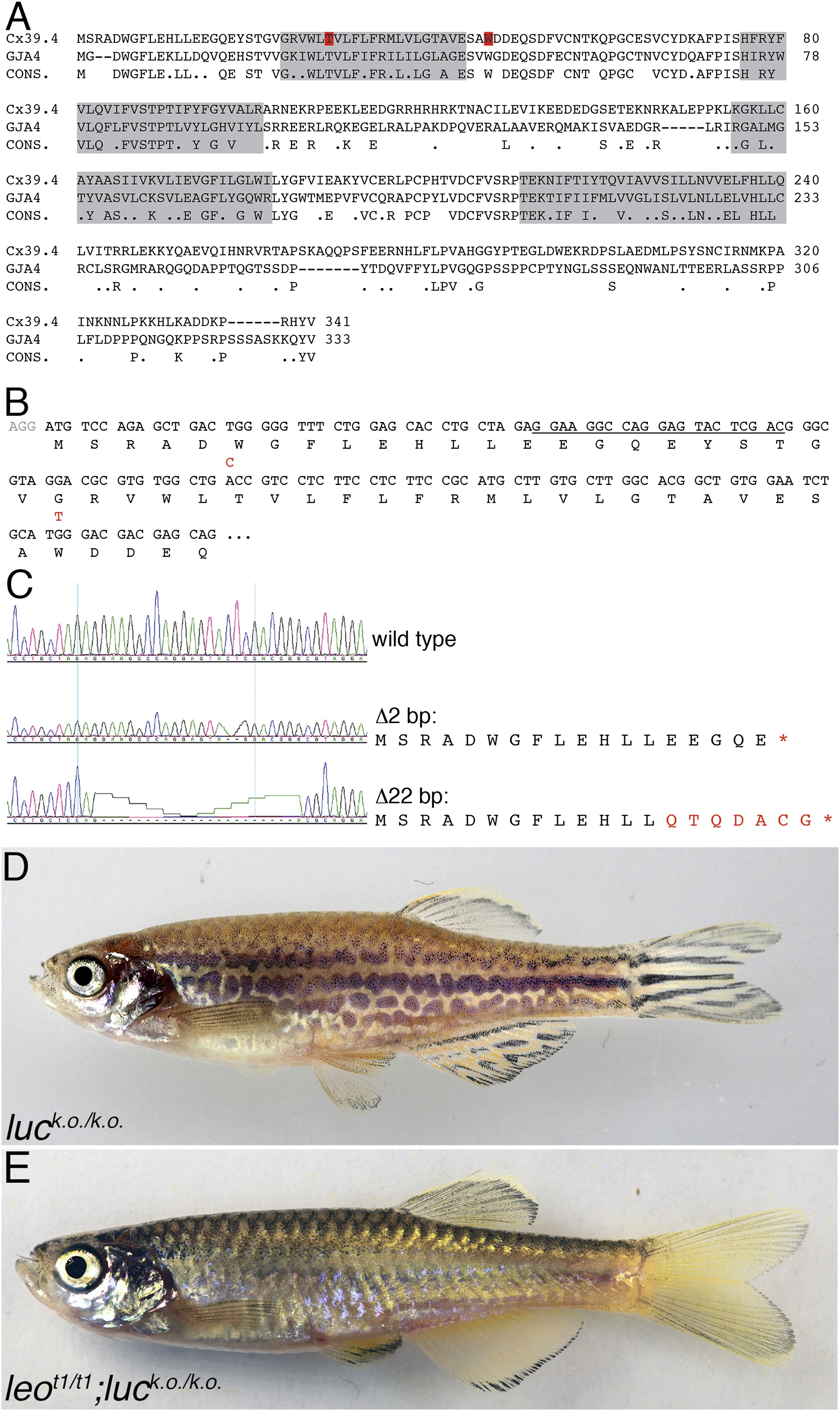
A comparison of the amino acid sequences of Cx39.4 of zebrafish, encoded by the luc gene, and human Cx37 (GJA4) is shown in (A). The transmembrane domains are shaded in grey, the residues mutated in luctXA9 (T29 P) and luctXG1 (W47 L) are highlighted in red. Note the extension of the N-terminal cytoplasmic domain of Cx39.4 by two amino acid residues. In (B) the beginning of the coding sequence for Cx39.4 is shown, the mutations in luctXA9 and luctXG1 are indicated in red above the sequence; the CRISPR target site is underlined. The sequence traces of wild-type fish and two fish homozygous for deletions of 2 and 22 bp are shown in (C). The predicted amino acid sequences for these mutants are indicated. In (D) a fish homozygous for the 2 bp deletion is shown, the striped pattern on the flank of the fish is disrupted and partly dissolved into spots, the fins are almost normal. Double mutants for leot1 and luc loss-of-function (E) have only very few melanophores on the flank and show an almost uniform pattern of iridophores and xanthophores.