Fig. 5
Acsl4a Regulates p38 MAPK Activity and R-Smad Linker Phosphorylation
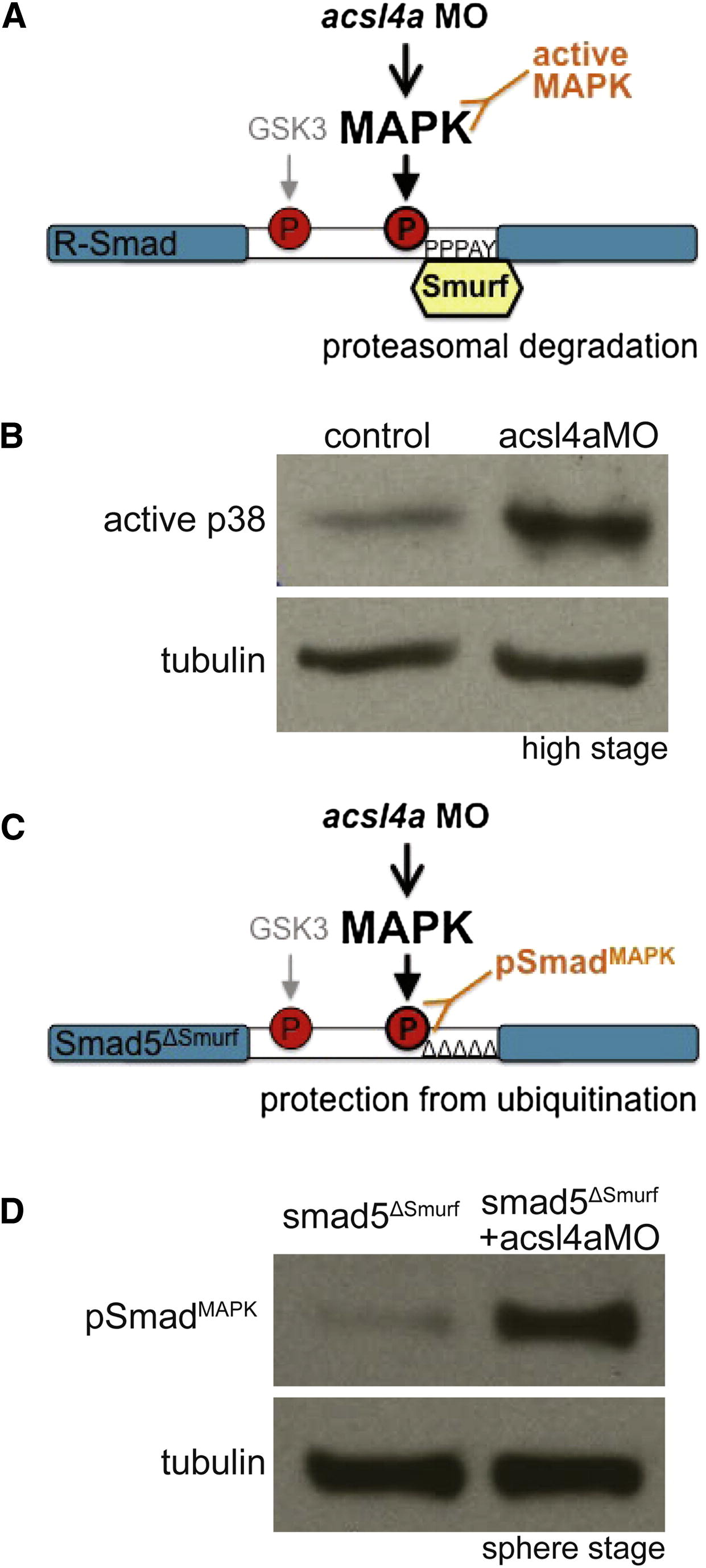
(A) An acsl4a MO-dependent increase in MAPK activity would result in phosphorylation of R-Smad and recruitment of Smurf ubiquitin ligase. An increase in MAPK activity can be assayed by antibodies specific to activated MAPK.
(B) p38 MAPK activity is upregulated in acsl4a morphants (750 fmol) at high stage. Western blot for phosphorylated (Thr180/Tyr182) p38 MAPK (active-p38 MAPK; n = 6).
(C) Smad5ΔSmurf lacks the WW domain-binding box (PPPAY→ΔΔΔΔΔ) recognized by Smurf E3 ubiquitin ligase, thus it is prevented from linker-mediated degradation. An increase in MAPK phosphorylation of R-Smad can be assayed with a phosphospecific antibody, pSmadMAPK.
(D) Smad5ΔSmurf is phosphorylated at the MAPK consensus site (Ser215) after acsl4a knockdown. Western blot for MAPK phosphorylated Smad (pSmadMAPK; gift of de Robertis) at sphere stage. acsl4a MO injection (750 fmol) results in increased pSmadMAPK staining. Alpha tubulin is the loading control.
See also Figure S6.
Reprinted from Developmental Cell, 27(6), Miyares, R.L., Stein, C., Renisch, B., Anderson, J.L., Hammerschmidt, M., and Farber, S.A., Long-Chain Acyl-CoA Synthetase 4A Regulates Smad Activity and Dorsoventral Patterning in the Zebrafish Embryo, 635-647, Copyright (2013) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Cell