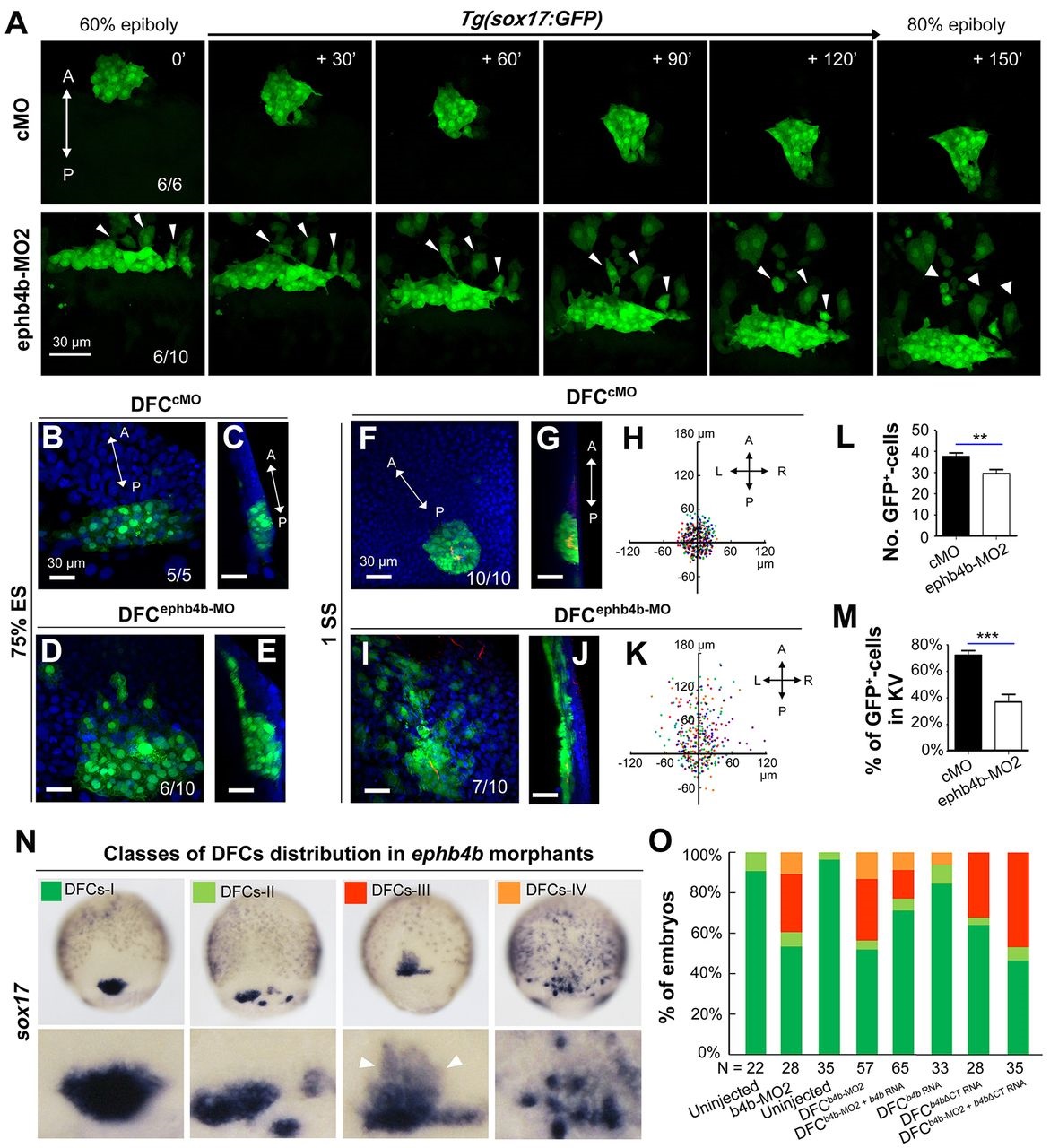
Fig. 3
DFC-specific ephb4b is required for DFC clustering. (A) Time-lapse confocal images showing DFC migration in Tg(sox17:GFP) living embryos injected with MO at the 512-cell stage. The ratio of embryos with the representative pattern is indicated. Arrowheads indicate DFCs moving away from the cluster. See also Movies 1 and 2. (B-E) Aggregation of DFCs. Tg(sox17:GFP) embryos injected at the 512-cell stage were immunostained at 75% ES for GFP (green) and nuclei (DAPI; blue). B and D, dorsal views; C and E, lateral views. Note that some GFP-positive DFC cells have involuted to form a string of hypoblast cells in the ephb4b morphant (E). (F-M) Aggregation of KV cells. Injected Tg(sox17:GFP) embryos were immunostained at 1 SS for GFP (green), aPKC (red) and nuclei (DAPI; blue). F and I, dorsal views; G and J, lateral views. Note the presence of DFC-derived GFP-positive cells outside KV in the ephb4b morphant (I,J). The distribution of individual GFP-positive cells from ten embryos is illustrated by projecting them on x- and y-axes with the aPKC-labeled KV lumen as the cross-point (H,K). The number of GFP-positive cells inside and close to KV (L) and the percentage of GFP-positive KV epithelia (labeled by aPKC) (M) in ten embryos were compared. **P<0.01; ***P<0.001. (N,O) Disruption of sox17-expresssing DFCs in ephb4b morphants. The representative DFC cluster patterns are shown in N and the proportion of embryos exhibiting each pattern category are presented in O. The AP axis is indicated in A-K.