Fig. 9
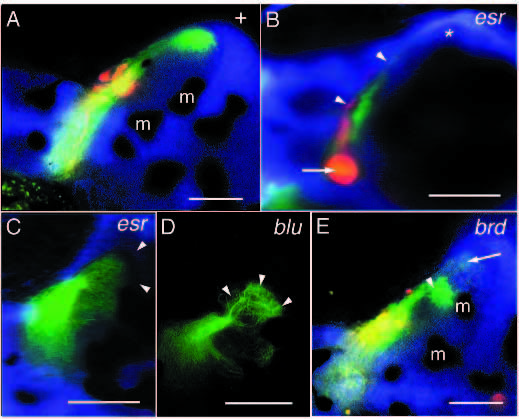
Mutations affecting the formation of termination fields. (A) Retinotectal projection of a wild-type fish. (B) Retinotectal projection of an esr mutant. Retinal axons form a thickening right behind the optic papilla (arrow). Although many axons are still seen in the optic tract, the termination fields of the RGC axons on the tectum are tiny (arrowheads). Nasodorsal axons are not seen in the posterior tectum (*). (C) Nasodorsal axons of esr. In this case, the nasodorsal axons reach the posterior margin of the tectum (approximate position marked by arrowheads). Their termination field is spread out and covers a larger area than usual. (D) Nasodorsal axons of blu. Upon reaching their target area in the posteroventral tectum, they arborize in a cauliflower-like fashion (arrowheads). (E) Retinotectal projection in a brd mutant. Many nasodorsal axons terminate prematurely already in the midventral tectum (arrowhead). Nasodorsal axons in the posteroventral tectum are marked by an arrow. m, melanophore. Scale bars, 0.1 mm.