Fig. 6 S1
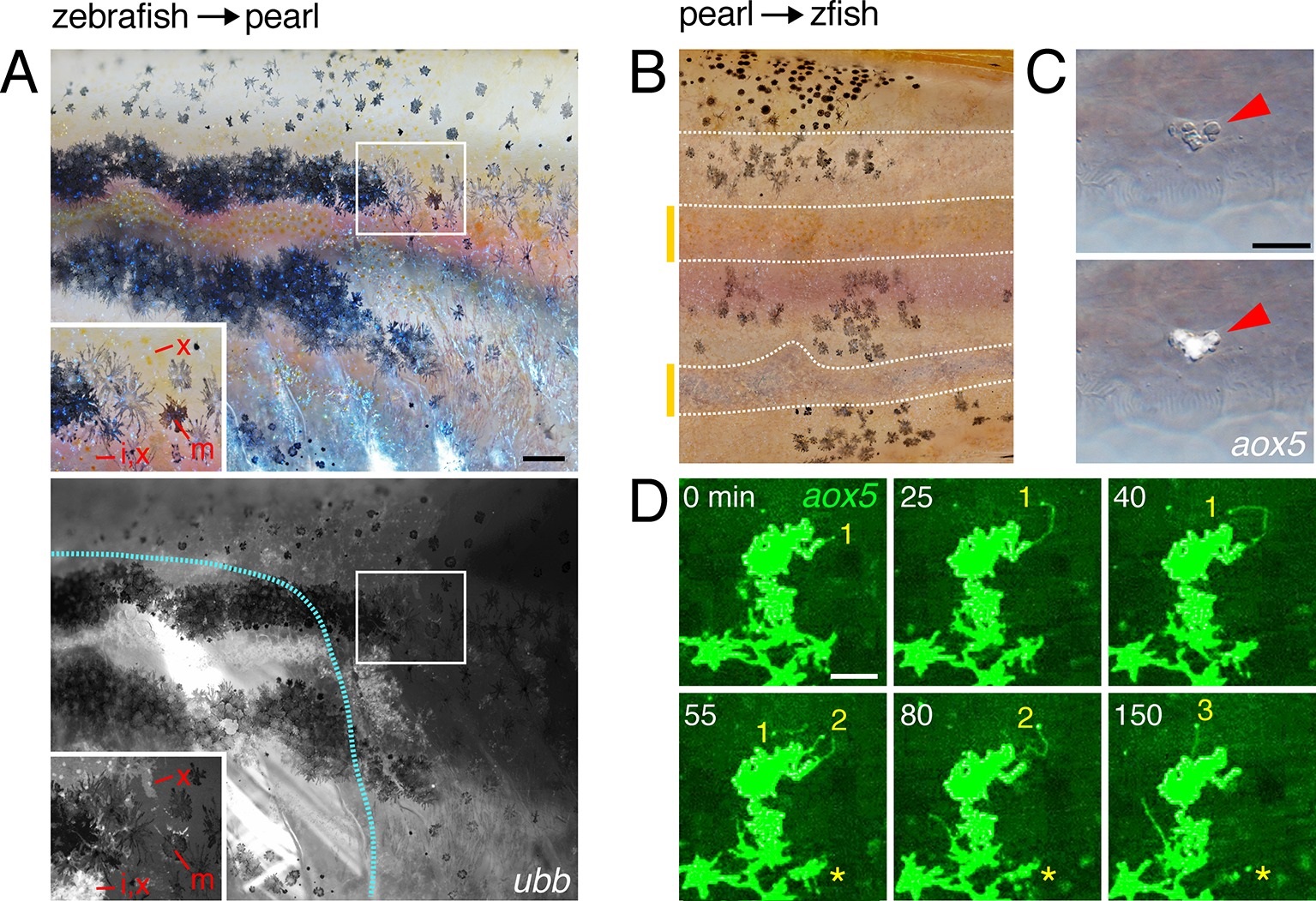
Interspecific chimeras reveal non-autonomous effects on pattern and aox5+ cell behaviors.(A) In zebrafish→pearl chimeras, well-organized stripes of zebrafish cells formed but only when all three classes of zebrafish pigment cells (inset: x, xanthophore; m, melanophore; i, iridophores) were present and in the vicinity of other zebrafish tissues (blue outline, donor myotomes). Ten adult chimeras analyzed. (B) In pearl→albino zebrafish chimeras (in which host melanophores were present but unpigmented), pearl melanophores were confined to stripes, adopting a zebrafish-like arrangement; stripe-interstripe boundaries are indicated by dashed white lines and interstripes by yellow-orange bars at left. (C) Pearl aox5+ cells frequently developed in zebrafish hosts at embryonic/early larval stages (N=90 aox5+ chimeras), yet these same cells typically died by prior to time-lapse imaging during adult pigment pattern formation, here apparent by fragmentation and extrusion of GFP+ debris, typical of pigment cell death in zebrafish (Lang et al., 2009; Parichy et al., 1999). (D) Prior to extrusion, rare, surviving pearl danio aox5+ cells could extend numerous airinemes in zebrafish hosts (3 airinemes are shown; *, aox5+ cell fragmenting during imaging). Scale bars: 100 Ám (A, for A and B); 20 Ám (C); 50 Ám (D).