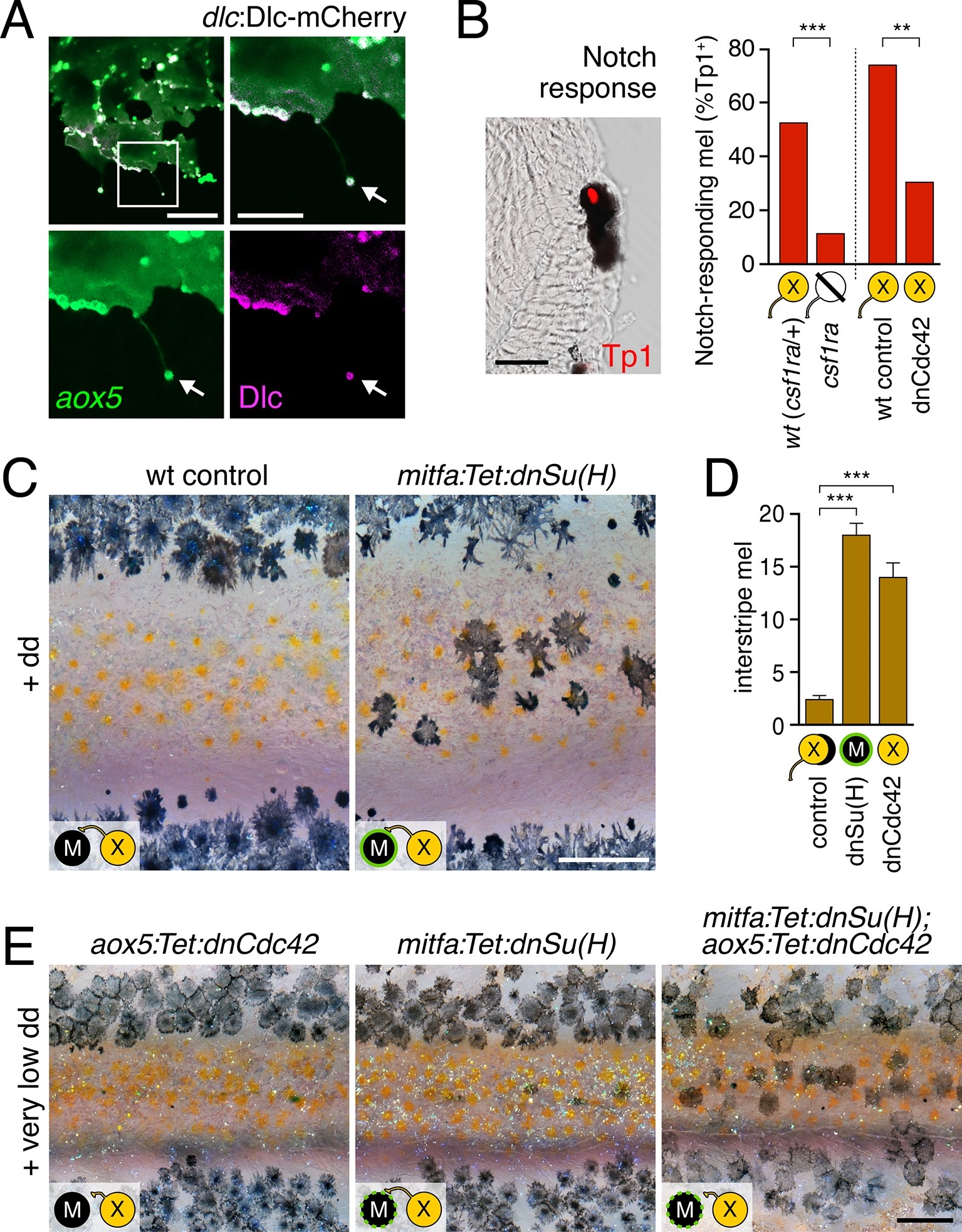
Fig. 5
Melanophore clearance requires airineme-dependent Notch signaling in melanophores.(A) aox5+ airineme vesicles harbored DlC-mCherry (arrow). (B) Frequencies of Tp1+ Notch-responding melanophores were reduced in the absence of aox5+ cells (csf1ra; χ2=15.5, d.f.=1, p<0.0001, N=77 cells) or airinemes (dnCdc42; χ2=9.0, d.f.=1, p<0.005, N=46 cells). Epidermal and muscle cells were also Tp1+ (not shown) but within the hypodermis, where pigment cells reside (Hirata et al., 2003), we observed only melanophores to be Tp1+. (C) Interstripe melanophores persisted when Notch signaling was blocked within the melanophore lineage by dnSu(H) [melanophore logo with green outlining], similar to dnCdc42 blockade of aox5+ airinemes (compare with Figure 4B). (D) Quantification of interstripe melanophores (mean ▒ SE) in dd-treated non-transgenic fish as well as mitfa:Tet:dnSu(H) and aox5:Tet:dnCdc42 (overall, F2,12=58.6, p<0.0001). (E) When induced with threshold levels of dd, persisting interstripe melanophores (means ▒ SE) were threefold more abundant (t7=2.9, p<0.05) in fish doubly transgenic for mitfa:Tet:dnSu(H) and aox5:Tet:dnCdc42 as compared to singly transgenic fish (shown at 9.8 SSL). Scale bars: 15 Ám (A, left); 10 Ám (A, right); 20 Ám (B); 200 Ám (C); 200 Ám (E).