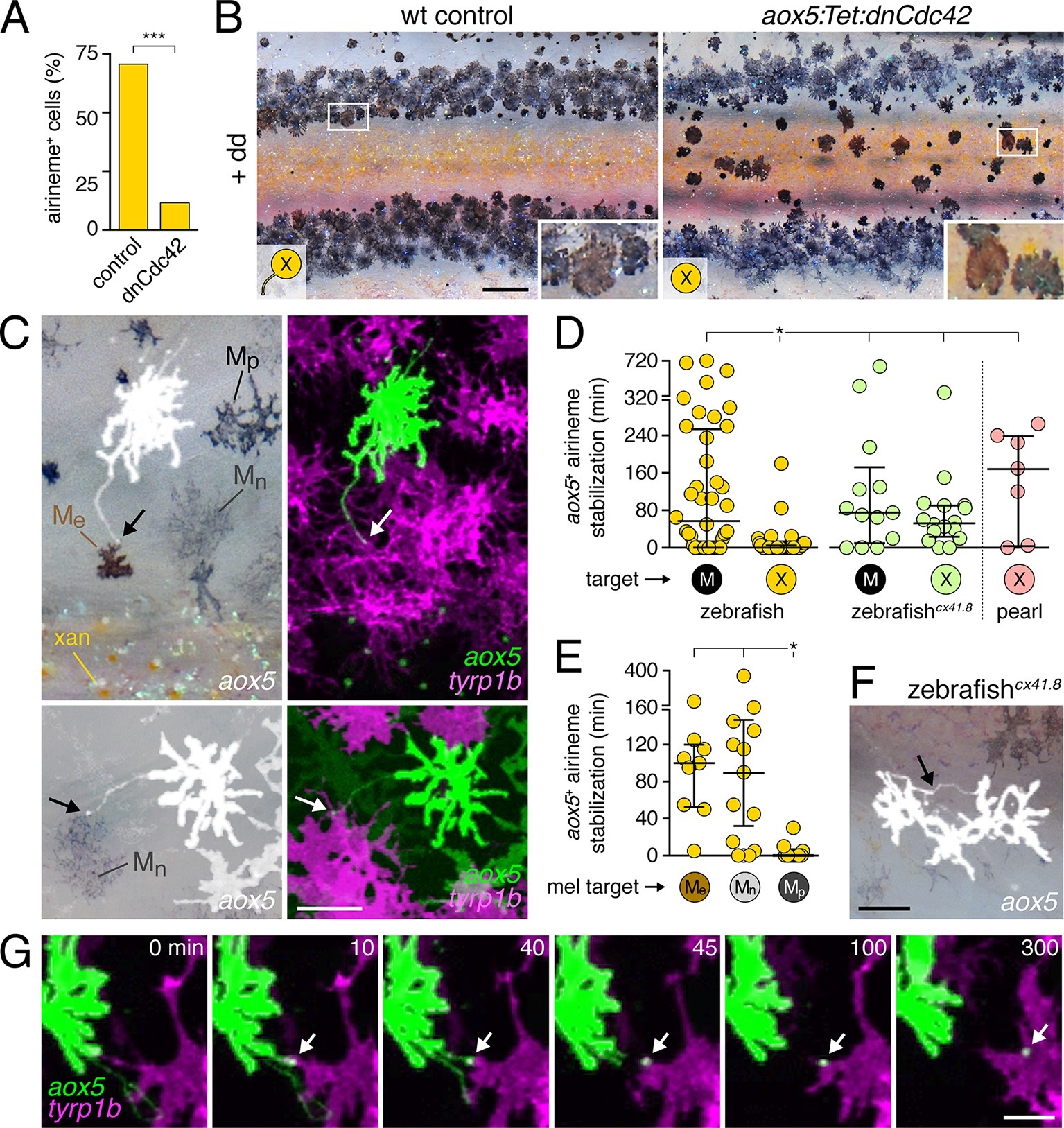
Fig. 4
Airineme dependent patterning and airineme targeting specificities.(A) dnCdc42 blocks airineme extension (χ2=16.4, d.f.=1, p<0.0001, N=43 cells total). (B) Interstripe melanophores persisted when airinemes were blocked with dnCdc42. Cell states are indicated by logos in lower left corners (X, aox5+ xanthophore lineage). Insets, brownish melanophores persisting from embryonic/early larval pattern and gray?black adult melanophores. (C) Airinemes contacting melanophores (arrows; Me, early larval; Mn, new; Mp, previously differentiated; xan, xanthophore). (D) Stabilization times (median ▒ IQR) of aox5+ airinemes on cells of melanophore (M) or xanthophore (X) lineages for zebrafish, cx41.8 mutant zebrafish, and pearl danio. aox5+ airinemes of wild-type zebrafish were less likely to stabilize, and stabilized more briefly (*, both p<0.0001) after contacting cells of the xanthophore lineage as compared to melanophores; this target specificity was altered in cx41.8 mutant zebrafish as well as pearl danio. Y-axis is split for clarity. (E) Zebrafish aox5+ airinemes were most likely to stabilize on Me and Mn (*, p<0.0001; median ▒ IQR). (F) cx41.8 mutant airinemes stabilized on aox5+ cells (arrow). (G) Vesicle transfer (arrow) to melanophore. Scale bars: 200 Ám (B); 50 Ám (C); 50 Ám (F); 25 Ám (G).