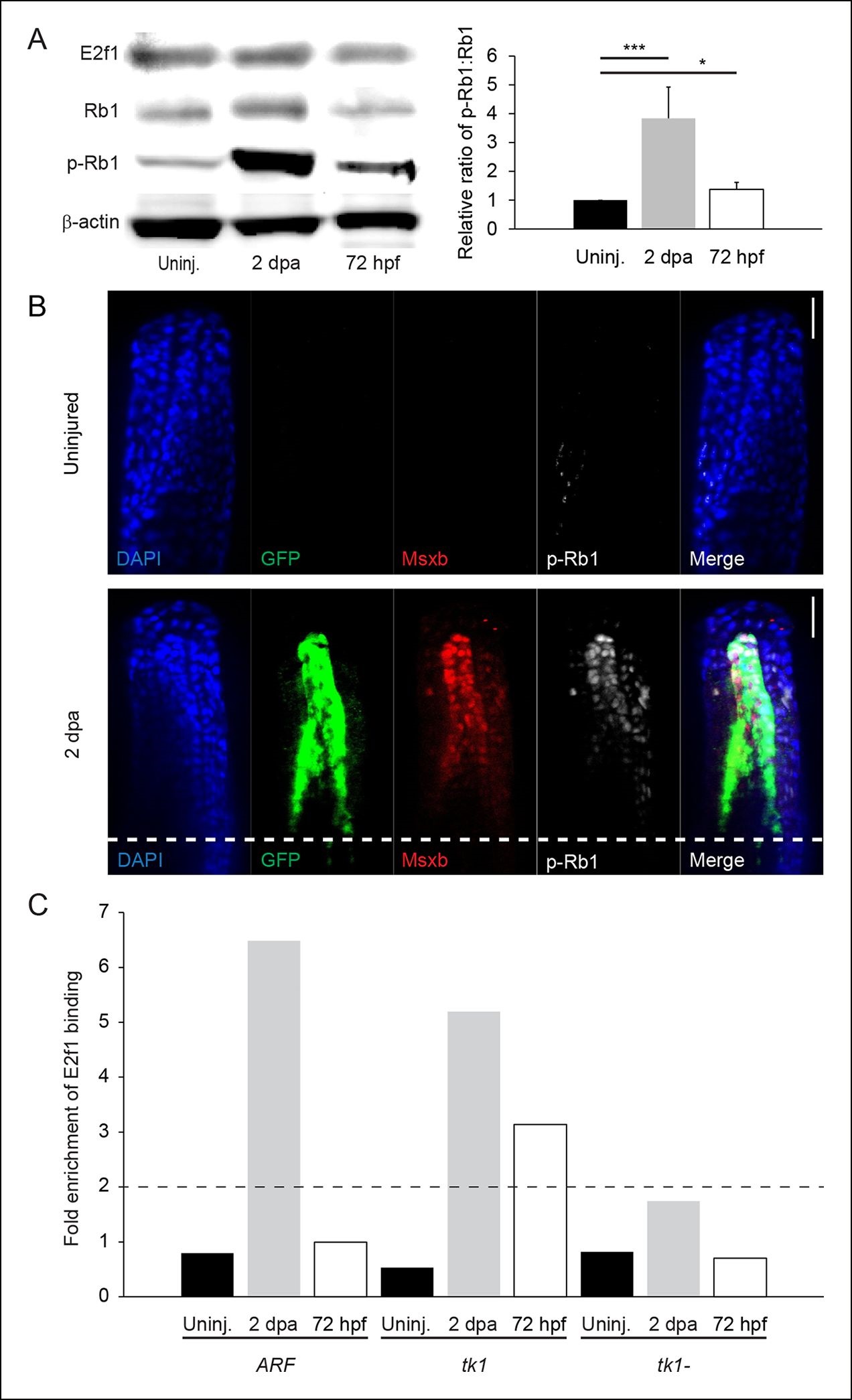
Fig. 2
Rb1 hyperphosphorylation and E2f1 binding of the human ARF promoter in the blastema during regeneration. (A) Representative Western blot of three experimental replicates of Rb pathway components, E2f1, Rb1, and hyperphosphorylated Rb1 (p-Rb1), before injury (uninj.), at 2 dpa, and during embryogenesis at 72 hpf (left). Quantification of p-Rb1 and Rb1 levels normalized to β-Actin and relative to uninjured tissue. Results are from three independent biological replicate experiments and are shown as mean ratios ▒ standard deviation. *p<0.05; ***p<0.001 (right). (B) Confocal images of coronal vibratome sections immunostained for Green fluorescent protein (GFP), Msxb, and p-Rb1 in uninjured and regenerating (2 dpa) ARF:GFP fins. Scale bars: 50 Ám. Very little p-Rb1 staining is seen in the uninjured fin, but high levels of p-Rb1 staining can be seen in Msxb + cells in the blastema at 2 dpa. The white dashed line represents the amputation plane. (C) Representative ChIP qPCR data of three experimental replicates with a pool of 30 fins per experiment. Tissue was collected from ARF:GFP transgenic fish before injury (uninj.), at 2 dpa (regenerate only), and at 72 hpf. Fold enrichment of E2f1 binding was normalized to rabbit IgG. The zebrafish thymidine kinase 1 (tk1) promoter was used as a positive control for E2f1 binding. Sequences 2 kbp upstream of tk1 were used as a negative control (tk1-). Values above twofold (black dashed line) are significant (p<0.05). Figure supplement 1 shows promoter sequences for the ARF, tk1, and tk1- promoters annotated for canonical E2f binding sites. hpa: Hours postamputation.