Fig. S6
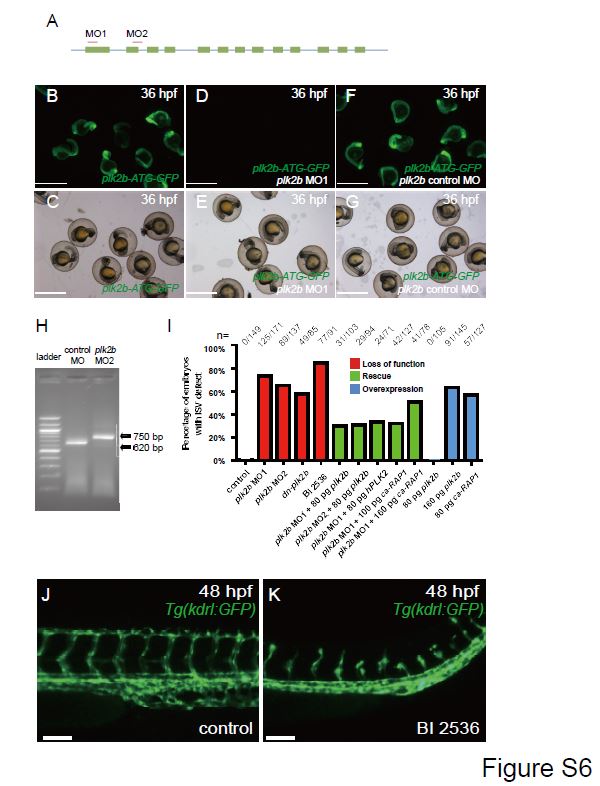
Loss of plk2b function causes endothelial cell sprouting defects. (A) The following regions of plk2b were targeted to create the plk2b ATG (MO1) and splice (MO2) morpholinos (MO). The blue line indicates the 5′UTR, introns and 3′UTR. The green boxes indicate the exons. (B?G) plk2b MO1 blocks GFP expression from a construct in which the target sequence is placed upstream of the GFP coding sequence (plk2b-ATG-GFP). (B, C) RNA injected from the plk2b-ATG-GFP construct results in GFP expression throughout the embryo (n=31/31 GFP+). (D, E) Injection of the plk2b MO1 reduced the green signal of the fused plk2b ATG-GFP RNA (n=0/44 GFP+). (F, G) Injection of the plk2b mismatch control MO failed to reduce the green signal of fused plk2b ATG-GFP RNA (n=41/41 GFP+). (B, D, F) GFP fluorescence microscopy. (C, E, G) Brightfield microscopy. Scale bar ? 1.5 mm. (H) Gel electrophoresis image shows that the plk2b splice MO2 blocks the proper splicing of plk2b and results in a larger 750 bp amplicon because of the inclusion of intron 2. Sanger sequencing of this amplicon showed an in-frame stop codon at the beginning of intron 2, which would block the translation of the rest exons of plk2b mRNA. Lane 1 ? 100 bp ladder, Lane 2 ? control MO, Lane 3 ? MO2. (I) Loss of Plk2b function (plk2b MO1, plk2b MO2, dn-plk2b mRNA, BI 2536 treatment) results in an increased percentage of embryos with ISV defect. However, co-injection with zebrafish plk2b RNA (plk2b MO1+80 pg plk2b and plk2b MO2+80 pg plk2b), human PLK2 RNA (plk2b MO1+hPLK2), or ca-RAP1 RNA (plk2b MO1+100 pg ca-RAP1) can rescue this vascular defect as seen by the reduced percentage of ISV defects in plk2b MO embryos. Although injecting 80 pg of plk2b RNA did not result in ISV defects, injecting 160 pg of plk2b or 80 pg of ca-RAP1 RNA results in an increased percentage of embryos with ISV branching defects. n indicates the number of embryos with vascular phenotype/total number of embryos injected or treated for each condition. (J, K) Treating Tg(kdrl:GFP) fish with the PLK inhibitor, BI 2536, at 20 hpf decreased endothelial cell sprouting at 48 hpf (n=77/91) when compared to DMSO treated fish (n=0/43). Top, dorsal longitudinal anastomotic vessel; bottom, dorsal aorta/cardinal vein. Scale bar ? 80 Ám.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 404(2), Yang, H., Fang, L., Zhan, R., Hegarty, J.M., Ren, J., Hsiai, T.K., Gleeson, J.G., Miller, Y.I., Trejo, J., Chi, N.C., Polo-like kinase 2 regulates angiogenic sprouting and blood vessel development, 49-60, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.