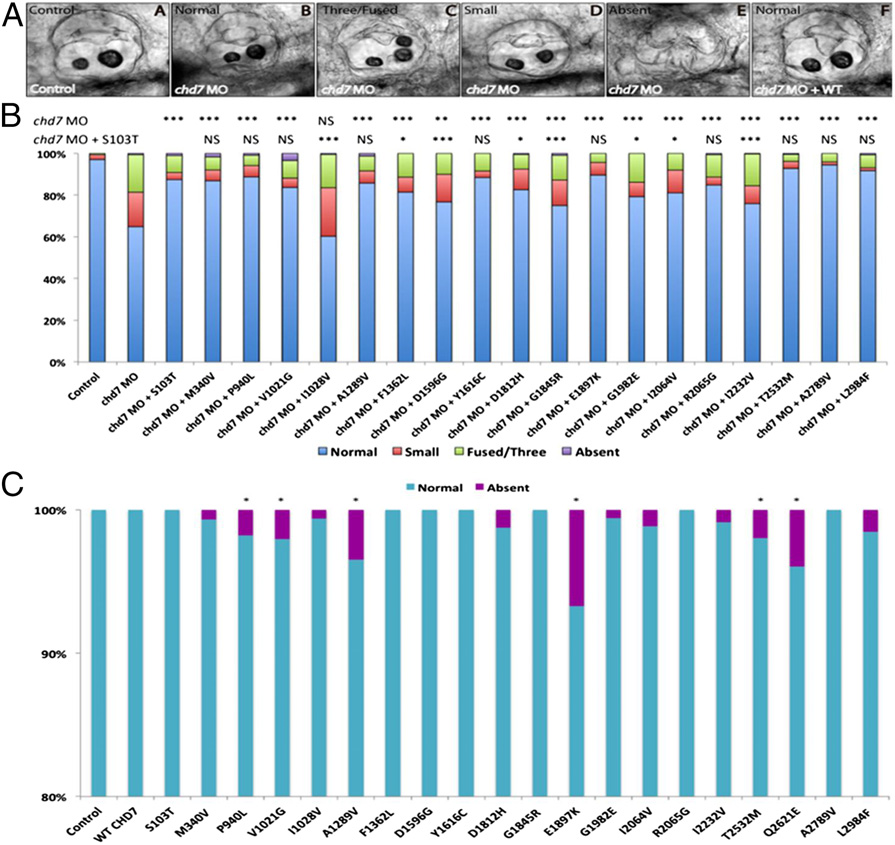
Fig. 2
Functional assessment of CHD7 RSVs in zebrafish assay. (A) The otic vesicle of control-MO?injected zebrafish contains two otoliths (Inset A). Larva treated with an MO against chd7 show normal (Inset B), three/fused (Inset C), or small (Inset D) or absent (Inset E) otoliths, whereas coinjection of WT human CHD7 rescues the morphant phenotype showing normal two otoliths (Inset F). (B) In vivo rescue assay: Coinjection of human CHD7 mRNA encoding mutant S103T allele along with chd7 MO results in significant rescue of morphant phenotype indistinguishable from WT rescue. Coinjection of chd7 MO with human CHD7 mRNAs encoding the two other control alleles (p.M340V, p.L2984F) from group A (see main text) shows rescue similar to S103T allele. Five IGD-associated CHD7 alleles (p.F1362L, p.G1845R, G1982E, p.I2064V, and p.I2232V) from group B (see main text) were partial LOF alleles (hypomorphs). Of the CHARGE-associated CHD7 alleles (group C, see main text), one was complete LOF (null) (p.I1028V) and two were hypomorphic (p.D1596G and p.D1812H). The remaining CHD7 alleles were benign on the rescue assay. (C) Overexpression of human mutant CHD7 mRNAs in zebrafish: overexpression of the human WT CHD7 mRNA did not induce any appreciable phenotypes. Four IGD-associated CHD7 alleles (p.P940L, p.E1897K, p.T2532M, and p.Q2621E) from group B (see main text) and two CHARGE-associated CHD7 alleles (p. A1289V and p.V1021G) from group C (see main text) showed a dominant effect in the overexpression assay. The remaining CHD7 alleles were benign on the overexpression assay. ***P < 0.0005, **P < 0.005, *P < 0.05; NS, not significant.