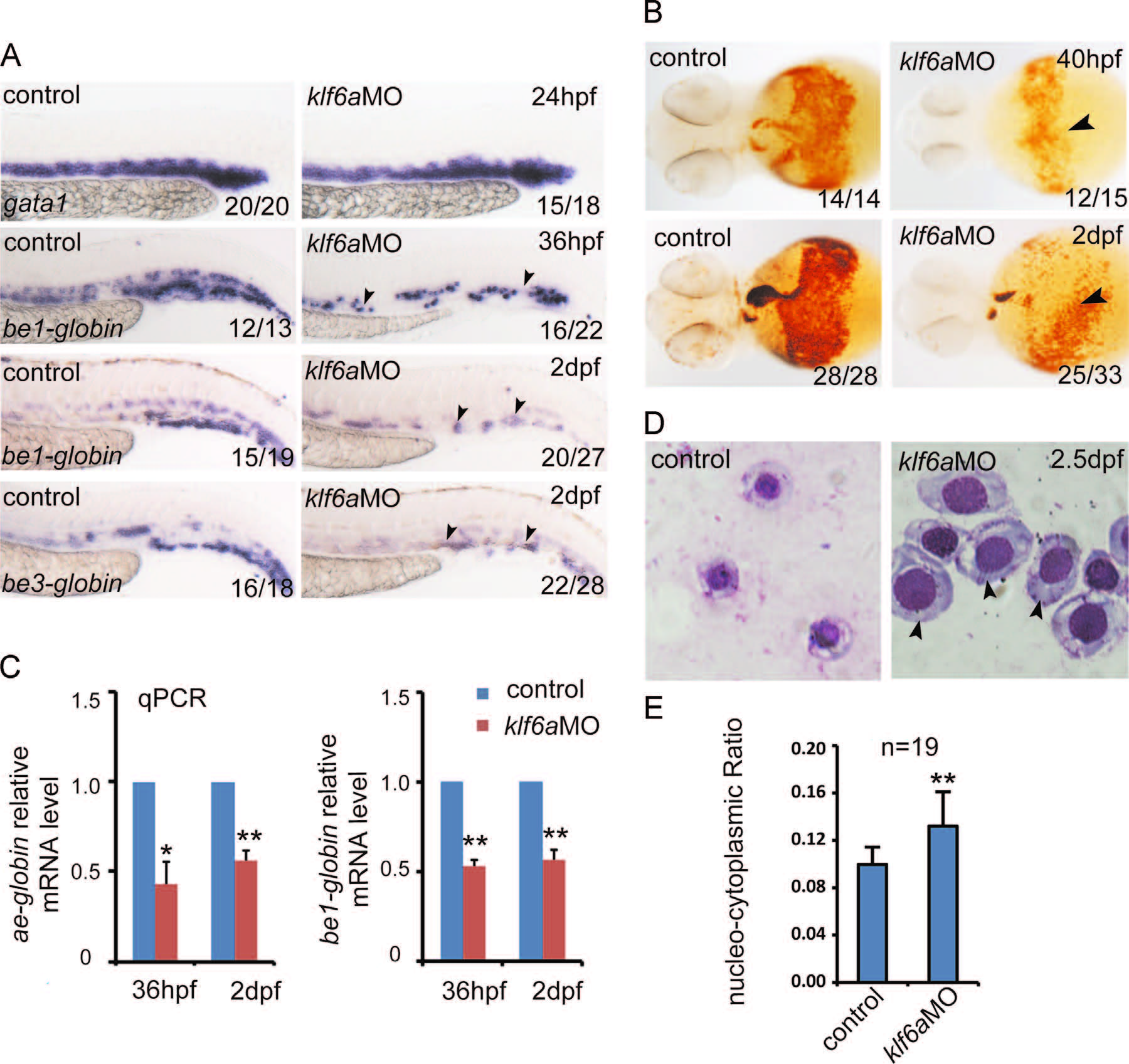
Fig. 5
klf6a knockdown induces a blockage of erythroid cell differentiation and maturation. (A) WISH results showed that gata1 expression was comparable between controls and klf6a morphants from 24 hpf. The expression of be1-globin and be3-globin was decreased in klf6a morphants, compared with controls at 36 hpf and 2 dpf. (B) The number of o-dianisidine-positive cells (marked by arrowheads) decreased dramatically in klf6a morphants between 40 hpf and 2 dpf. (C) The real time PCR results displayed that ae1-globin and be1-globin were downregulated in klf6a morphants at 36 hpf and 2 dpf (meanąSD, *P <0.05, **P <0.01, n=3). (D) Giemsa staining of erythroid cells from the blood of controls and klf6a morphants at 2.5 dpf. The size and nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio of red blood cells in klf6a morphants were noticeably larger than those of controls. The arrowhead marks the delayed erythroid progenitor. (E) Quantification of the nucleo-cytoplasmic ratio between controls and klf6a morphants (meanąSD, NNP <0.01, n=19).
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 403(2), Xue, Y., Gao, S., Liu, F., Genome-wide Analysis of the Zebrafish Klf Family Identifies Two Genes important for Erythroid Maturation, 115-27, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.