Fig. 2
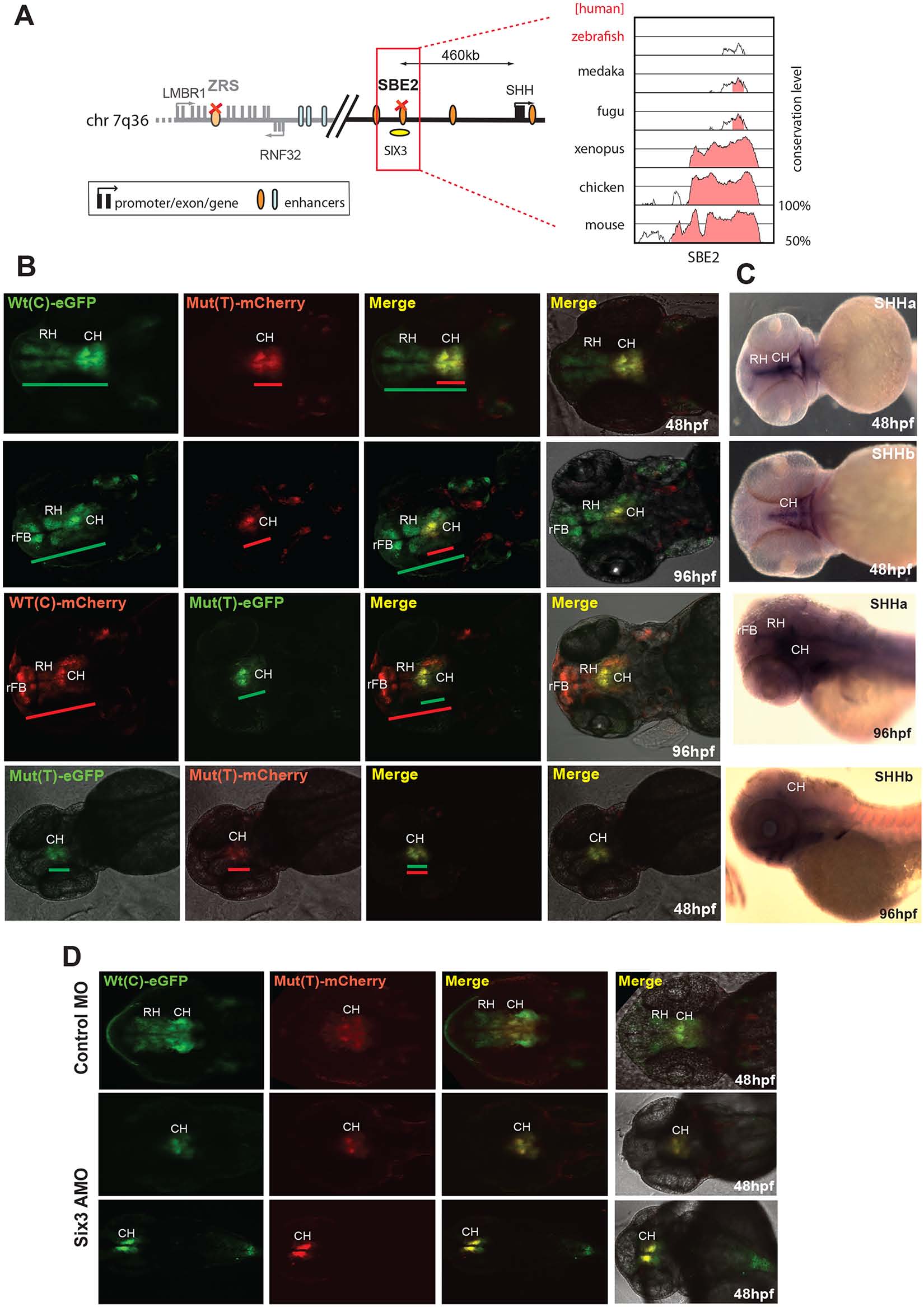
Duel-florescence transgenic analysis of a SHH enhancer SBE2 where a C>T change in a Six3 binding site has been identified in a patient with holoprosencephaly.
(A) Regulatory landscape of SHH, depicting the location of the SBE2 enhancer. The sequence conservation plot on the right shows the low level of sequence conservation for SBE2 in the zebrafish genome. (B) SHH-SBE2 enhancer-driven F1 reporter transgenics. The wild-type allele Wt(C) drives expression in the rostral and caudal hypothalamus (long green or red bar) independent of the associated fluorophore (eGFP or mCherry). Expression from the mutant allele, Mut(T), is retained in the caudal hypothalamus (short green or red bar) but lost in the rostral hypothalamus (short green or red bar). Additional expression of the SBE2 Wt(C) allele in the rostral forebrain of later stage (96hpf) zebrafish embryos is also lost by the Mut(T) allele. (C) RNA in situ hybridisation analysis of shha and shhb expression at 48hpf and 96hpf of zebrafish embryonic development. The reporter gene expression pattern driven by Wt(C) allele significantly overlaps with the shha expression domain in the hypothalamus. (D) Morpholino knock-down of Six3 in SHH-SBE2 transgenic embryos mimics the effect of the Six3 binding site mutation in SBE2. F2 embryos bearing both SHH-SBE2 Wt(C) and Mut(T) alleles injected with either control morpholino (Control MO) or morpholino against both six3A and six3B (six3 AMO). Upon knockdown of six3, the hypothalamus expression driven by the Wt allele shrinks to overlap completely with the expression driven by the mutant allele (bearing a mutant six3 binding site). Wt: wild-type; Mut: mutant; hpf: hours post fertilization; MO: morpholino, RH: Rostral hypothalamus; CH: Caudal hypothalamus; rFB: Rostral forebrain.