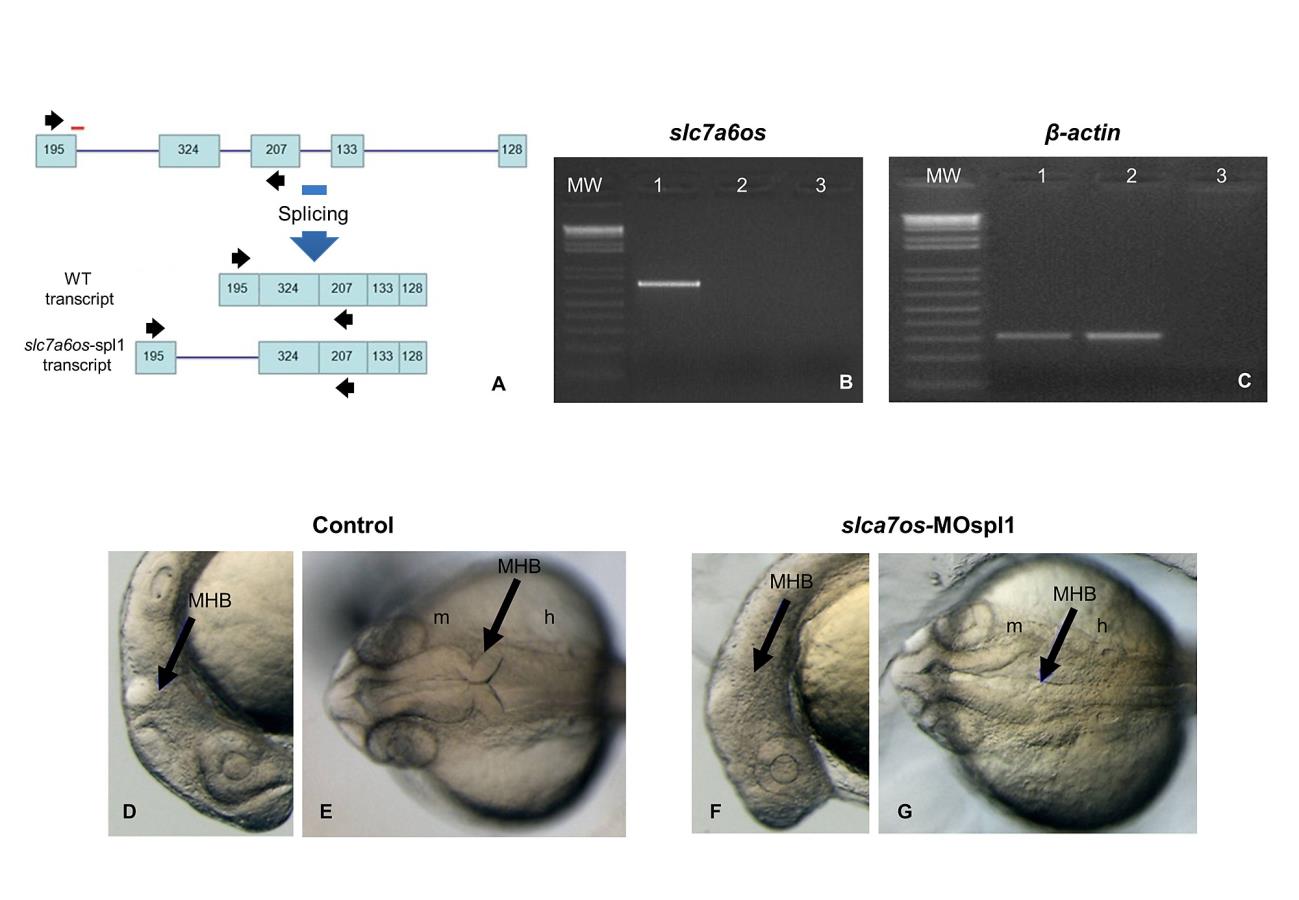
Fig. S4 The phenotypic effects of slc7a6os loss-of-function become evident at 24 hpf.
To knockdown the expression of a functional slc7a6os protein, the slc7a6os-MOspl1 splice blocking morpholino was synthesized targeting the exon1-intron1 boundary (A, red bar). RT-PCR experiments were performed on RNA extracted from slc7a6os-MOspl1-injected and control embryos with slc7a6os oligonucleotides on exon 1 and 3 (black arrows in A). The expected wild-type 681 bp PCR fragment is present only in control embryos (B, lane 1) and not detectable in slc7a6os-MOspl1 morphants (B, lane 2). The injection of slc7a6os-MOspl1 is expected to cause insertion of intron 1, leading to the production of a mature mRNA with several in frame termination codons after the coding sequence of exon 1. As anticipated, we failed to observe the predicted 3368 bp product in the RT-PCR analysis (B, lane 2) likely due to both the large size of the fragment to be amplified and the rapid degradation of the aberrant mRNA operated by the nonsense mediated decay mechanisms. A RT-PCR amplification was carried with β-actin primers as a quality control for both cDNAs. The lane 3 in panels B and C correspond to a RT-PCR reaction performed with no cDNA. At 24 hpf slc7a6os MO injected embryos exhibit CNS malformations with unclear boundaries between developing brain regions, especially at midbrain-hindbrain and hindbrain-midbrain boundaries (F, lateral view; G, dorsal view). The arrowheads indicate the midbrain-hindbrain boundary. Abbreviations: h, hindbrain; m, midbrain, MHB, midbrain-hindbrain boundary.