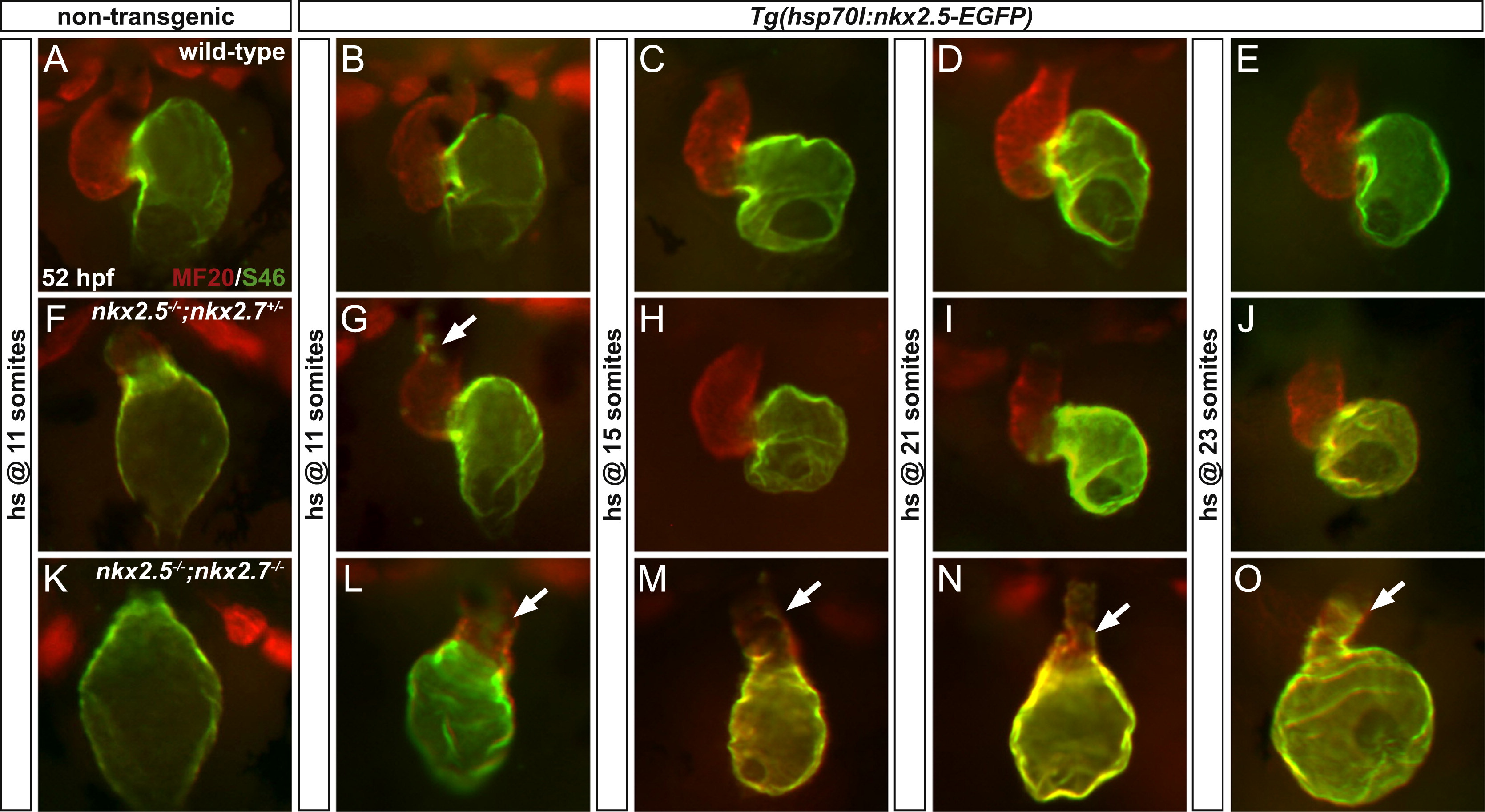
Fig. 5
Resupplying nkx2.5 in nkx2.5/;nkx2.7/ embryos reveals dose-dependent functions of nkx genes. Frontal views, anterior to the top, of MF20/S46 immunofluorescence (as in Fig. 3) at 52 hpf. In non-transgenic wild-type (A) and Tg(hsp70l:nkx2.5-EGFP) embryos (B-E), cardiac morphology and chamber-specific identity are maintained following heat shock at 11 somites through 23 somites. In contrast, non-transgenic nkx2.5-/-;nkx2.7+/- (F) and nkx2.5-/-;nkx2.7-/- (K) embryos have enlarged atrial chambers, underdeveloped or indiscernible ventricular chambers, and diminished outflow tracts. Following heat shock at the same time points as performed in the wild-type embryos, transgenic nkx2.5-/-;nkx2.7+/- embryos (G-J) exhibit substantial improvement in ventricular chamber size with only a few residual ectopic S46+ cardiomyocytes remaining in embryos treated at 11 somites (G). However, only moderate rescue of abnormalities in morphology and identity is achieved in the transgenic nkx2.5-/-;nkx2.7-/- embryos following heat shock at 11 somites and 15 somites (L,M) and only minimal rescue is achieved following heat shock at 21 somites and 23 somites (N,O). White arrows indicate ectopic S46+ cardiomyocytes.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 400(1), George, V., Colombo, S., Targoff, K.L., An early requirement for nkx2.5 Ensures first and Second heart field ventricular identity and cardiac function into adulthood, 10-22, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.