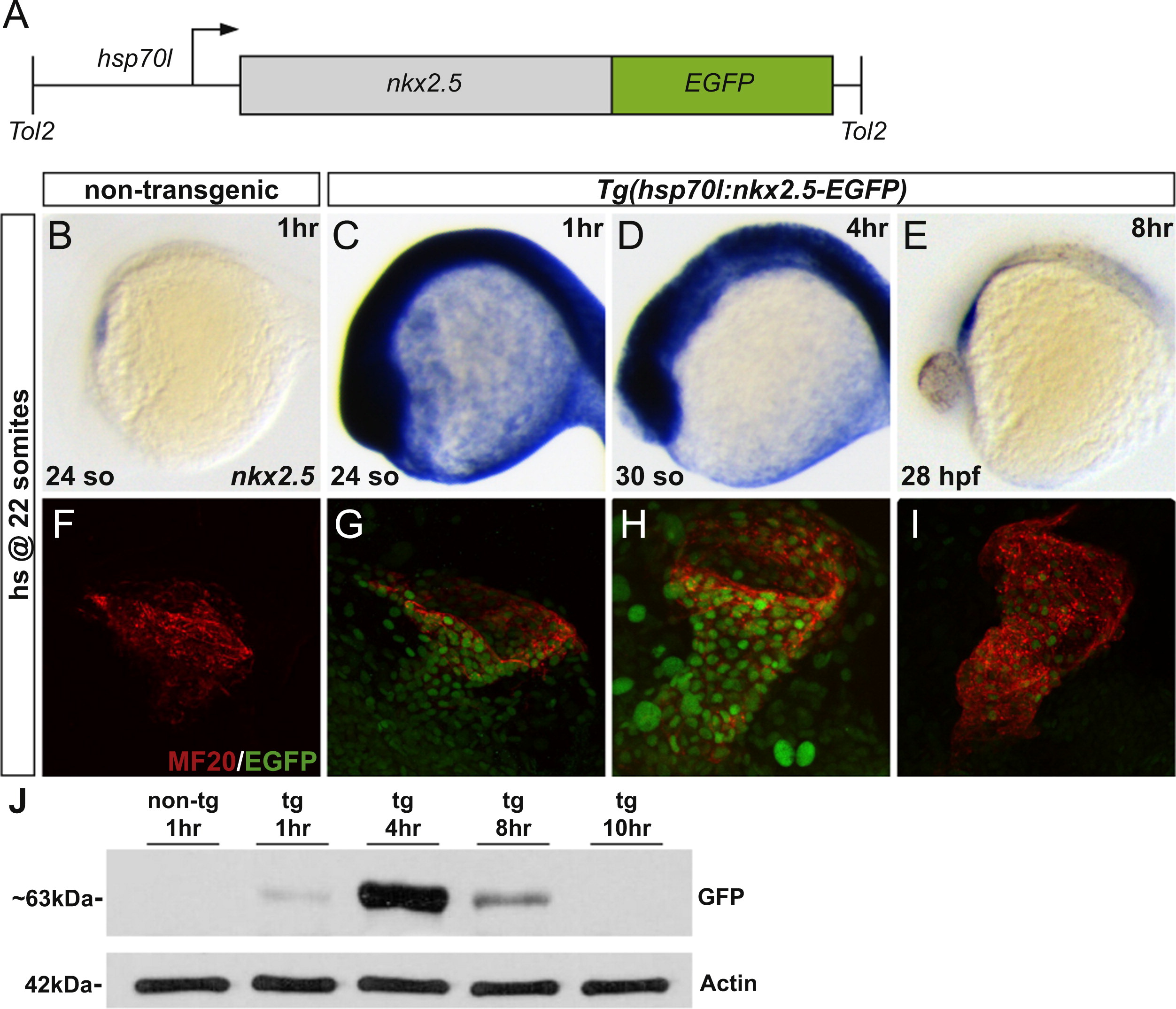
Fig. 1
Heat-shock inducible transgene, Tg(hsp70l:nkx2.5-EGFP), allows for temporally controlled expression of nkx2.5. (A) Schematic representation of the heat-shock inducible transgene. (B-E) In situ hybridization depicts expression of nkx2.5 in non-transgenic (B) and Tg(hsp70l:nkx2.5-EGFP) (C-E) embryos. Lateral views, anterior to the left. Following initiation of heat shock (hs) at 22 somites (20 hpf), non-transgenic embryos demonstrate endogenous nkx2.5 expression in the heart tube at 24 somites (1 h post-hs) (B). In comparison, heat-shocked transgenic embryos reveal upregulation of nkx2.5 ubiquitously in the embryo at 24 somites (1 h post-hs) (C) and at 30 somites (4 h post-hs) (D). By 28 hpf (8 h post-hs), global nkx2.5 expression is significantly diminished and only cardiac specific expression remains (E). Time interval post-hs is indicated in the upper right corner of each panel. (F?I) MF20 immunofluorescence (red) indicates cardiac myosin heavy chain in all cardiomyocytes and EGFP (green) reflects transgenic expression following initiation of heat shock at 22 somites (20 hpf). Lateral views, anterior to the right. Confocal projections of fixed, dissected non-transgenic (F) and transgenic (G?I) hearts. EGFP can be visualized as early as 24 somites (1 h post-hs) (G) with strong perdurance through 30 somites (4 h post-hs) (H). Yet, only minimal residual expression is evident by 28 hpf (8 h post-hs) (I). (J) Western blots using anti-GFP and anti-Actin on protein extracts prepared from non-transgenic and transgenic embryos following heat shock. Samples were collected at 1 h, 4 h, 8 h, and 10 h post-hs, respectively. The full-length Nkx2.5-EGFP runs with apparent molecular weight of ~63 kDa. The same membrane was probed with anti-Actin, serving as a loading control.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 400(1), George, V., Colombo, S., Targoff, K.L., An early requirement for nkx2.5 Ensures first and Second heart field ventricular identity and cardiac function into adulthood, 10-22, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.