Fig. S6
Fig. S6
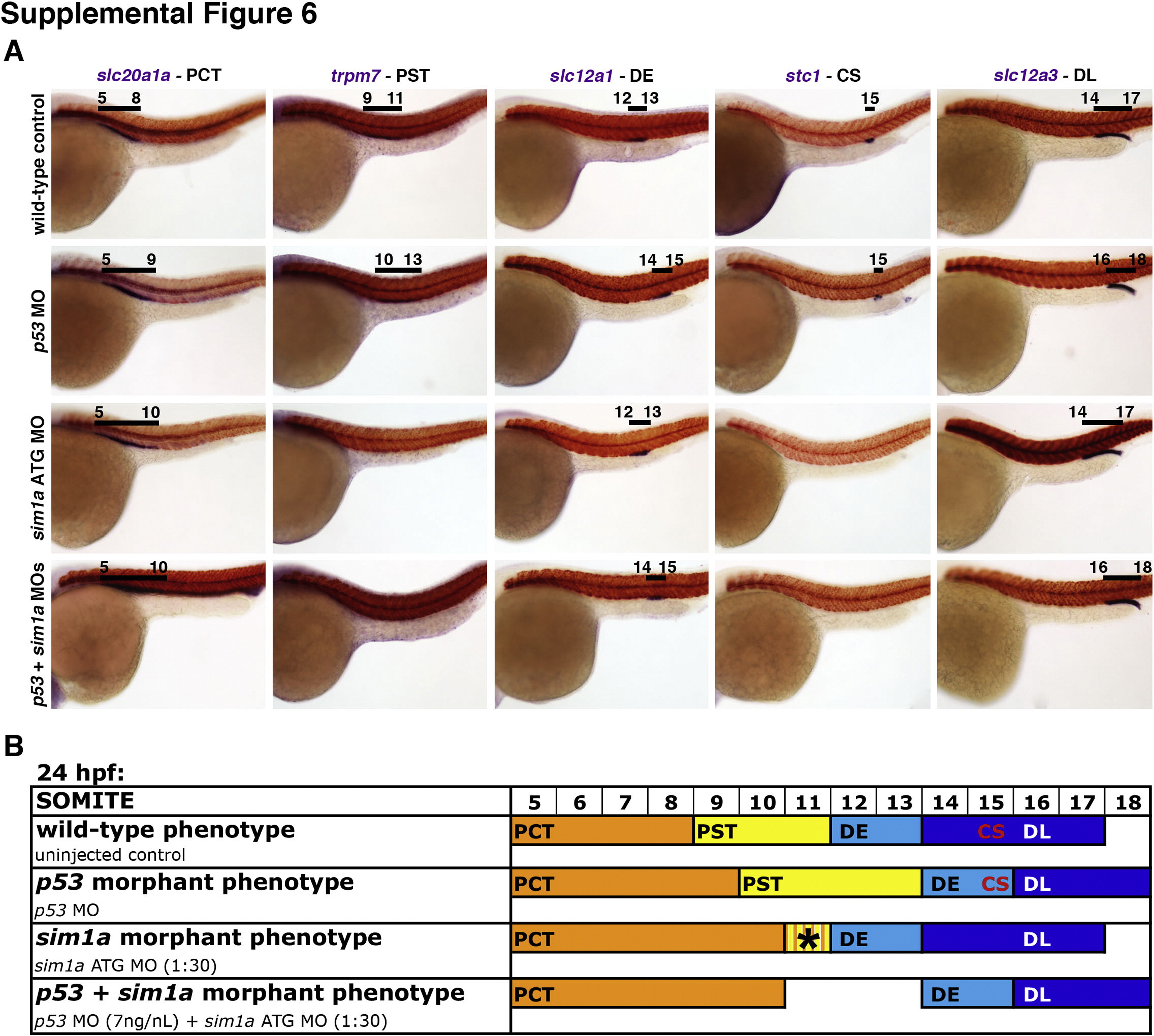
Nephron segmentation analysis in p53 morphants and after dual genetic knockdown of p53+sim1a reveals a role for cell death in embryonic renal development. (A) Segmentation patterning changes within the pronephros of wild-types, p53 morphants, sim1a ATG morphants, and combined p53+sim1a morphants were independently assessed. WISH of embryos at 24 hpf indicates the expression of specific kidney segment markers (purple) in relation to the smyhc1-expressing somites (red). Black lines with corresponding somite numbers indicate segment domains. Embryo anterior is to the left in all panels. (B) Diagram indicates the dominant segmentation phenotypes displayed by wild-type control embryos and the various morphants at 24 hpf. Colored bars indicate the respective domains of each nephron segment in relation to the somite numbers located above. The striped region of PCT/PST within the colored bars indicates an area with lower as well as variable transcript expression. Abbreviations: CS ? corpuscles of Stannius; DE ? distal early; DL ? distal late; hpf ? hours post fertilization; MO ? morpholino; PCT ? proximal convoluted tubule; PST ? proximal straight tubule; WISH ? whole mount in situ hybridization.
Reprinted from Developmental Biology, 399(1), Cheng, C.N., Wingert, R.A., Nephron proximal tubule patterning and corpuscles of Stannius formation are regulated by the sim1a transcription factor and retinoic acid in zebrafish, 100-16, Copyright (2015) with permission from Elsevier. Full text @ Dev. Biol.